Fig. 3.
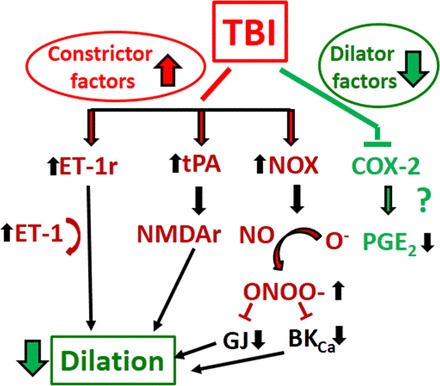
Proposed mechanisms underlying impaired myogenic autoregulatory protection after TBI: TBI-induced decreased myogenic dilation. TBI impairs the capability of cerebral vessels to dilate (thus to decrease cerebrovascular resistance) when PP drops. For detailed description of these pathways we refer to the text. BKCa, large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; NADPH ox, NADPH oxidase; GJ, gap junction; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate; NMDAr, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor; ET-1, endothelin-1; ET-1r, endothelin-1 receptor; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator.
