FIGURE 8.
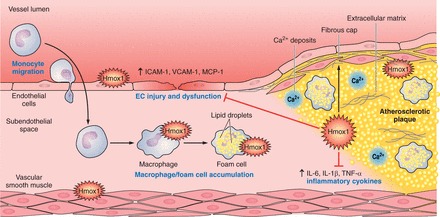
Potential modulatory roles of Hmox1 in atherogenesis. Hmox1 expression in macrophages, foam cells, EC, and VSMC has been associated with decreases in EC injury; EC dysfunction; expression of the adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and intracellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1); release of the inflammatory cytokines monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6; and decrease in oxidative damage. In addition, increased Hmox1 expression has been reported to increase the stability of atherosclerotic lesions.
