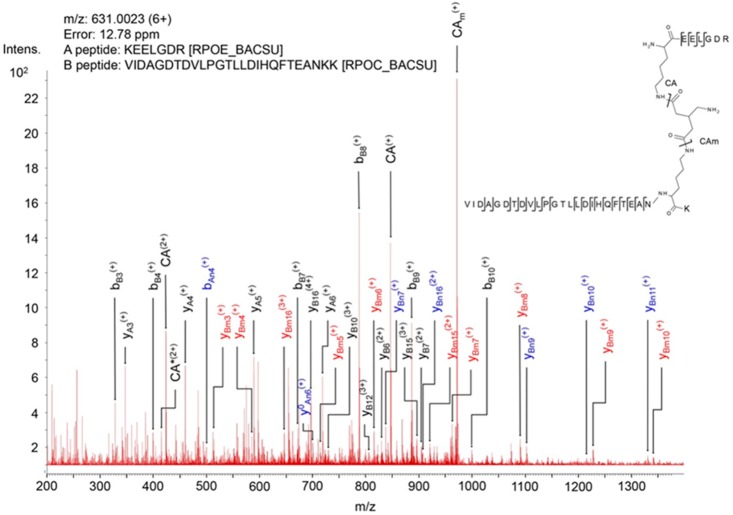
Figure 4.
Mass spectrum of product ions generated by collision-induced dissociation of a precursor ion of a BAMG-cross-linked peptide pair. The spectrum shows characteristic features of the fragmentation pattern of a cross-linked peptide in which the azido group in the spacer of the cross-linker has been reduced to an amine group. These features are (i) signals of high intensity resulting from cleavage of the cross-linked amide bonds leading to unmodified peptide A (CA) and peptide A modified by the remnant of the cross-linker in the form of a γ-lactam (CAm), adding 125.0477 Da to the mass of peptide, and (ii) secondary fragments resulting from cleavage of a cross-linked amide bond along with peptide bond cleavages of an unmodified peptide (blue, subscript An, Bn) or a peptide lactam (red, subscript Am, Bm). These secondary cleavages occur along with primary cleavages of the peptide bonds (black, subscript A, B). The presence of both primary fragments (resulting from cleavages of the cross-link amide bonds and peptide bonds) and secondary fragments tremendously facilitates the identification of cross-linked peptides according to the work flow schematically depicted in Figure 3b. *, fragment with NH3 loss.