Fig. 1.
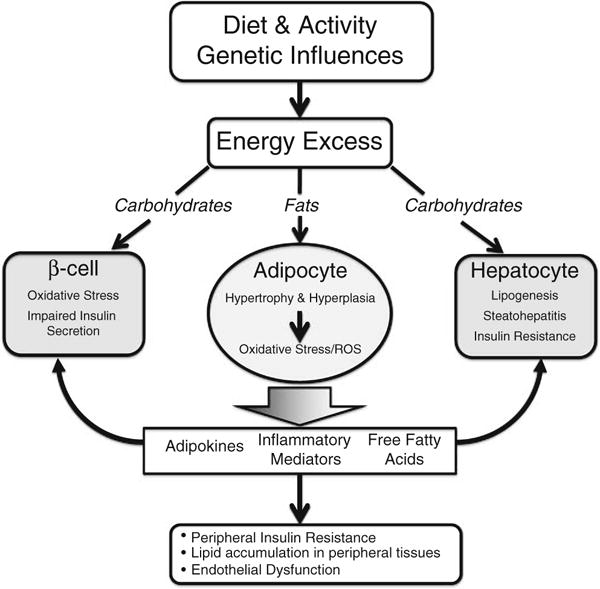
Energy excess, systemic inflammation and metabolic consequences. Excess dietary carbohydrates cause glucotoxicity and impaired insulin secretion in the pancreatic beta cell as well as steatohepatitis and insulin resistance in the hepatocyte. Excess dietary fats cause adipocyte hypertrophy and adipose hyperplasia, which leads to oxidative stress and altered production of adipokines and inflammatory mediators as well as increased circulating free fatty acids. This leads to a generalized inflammatory state and lipid accumulation in muscles, liver, vascular tissue, heart and beta cells. Adapted from reference [204]
