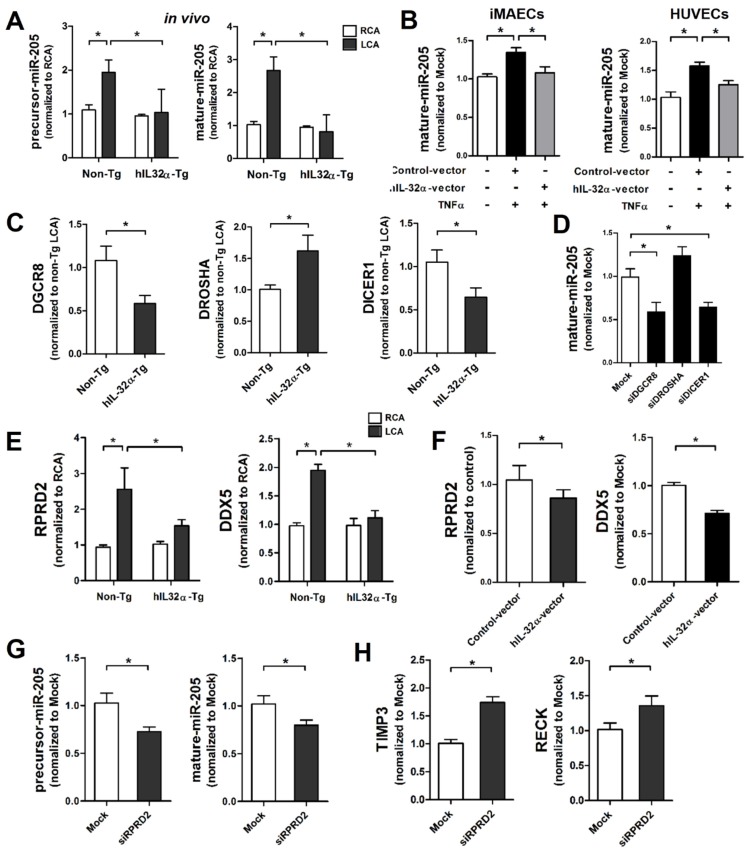
Figure 8.
IL-32α inhibits microRNA-205 expression by regulating microRNA biogenesis. (A) Expression of precursor and mature forms of miR-205 was determined by qPCR using endothelial-enriched RNA obtained from the LCA and RCA following partial carotid ligation in hIL-32α-Tg or non-Tg mice at 2 days post-ligation (n = 5 each). (B) iMAECs and HUVECs were cultured for 24 h, then transfected with human IL-32α-expressing pcDNA3.1+-6×Myc vector (hIL-32α-vector) or control vector. After 24 h, cells were treated with TNFα (10 ng/mL; 24 h), and the expression of mature miR-205 was determined by qPCR (n = 4). (C) Dgcr8, Drosha, and Dicer1 mRNA expression in mouse LCA (2 days post-ligation) was determined by qPCR (n = 5). (D) iMAECs were transfected with Dgcr8, Drosha, or Dicer1 siRNA (150 nM) for 24 h. The cells were then treated with TNFα and the expression of mature miR-205 was determined by qPCR (n = 5 each). (E) Rprd2 and Ddx5 expression in mouse RCA and LCA (2 days post-ligation) was determined by qPCR (n = 5). (F) iMAECs were transfected with hIL-32α or control vector. After 24 h, cells were treated with TNFα (10 ng/mL; 24 h), and Rprd2 and Ddx5 mRNA expression was determined by qPCR (n = 5 each). (G-H) iMAECs were transfected with Rprd2 siRNA (200 nM) for 24 h, and the expression of precursor and mature forms of (G) miR-205, and (H) Timp3 and Reck mRNA was determined by qPCR (n = 6 each). All data shown as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05 as determined by Student's t-test.