Fig. 2.
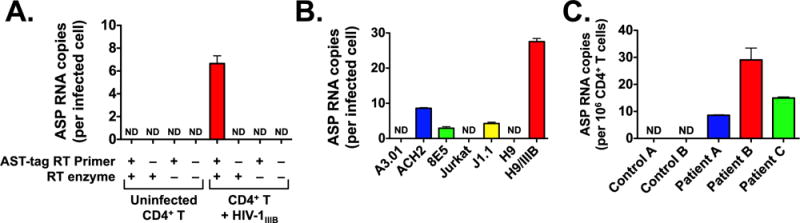
ASP RNA levels in various HIV-1 infected CD4+ T cell systems. Expression levels of the ASP transcript were assessed using the strand-specific, quantitative RT-PCR assay described in Fig. 1. Panel A: Quantification of ASP RNA expression in primary human CD4+ T cells infected in vitro. Total RNA from CD4+ T cells infected with HIV-1IIIB (or uninfected cells) was reverse transcribed with or without AST-tag RT primer, and with or without RT enzyme, and then tested by PCR in triplicate samples. Panel B: Quantification of ASP RNA expression in various chronically infected CD4+ T cell lines (ACH2, 8E5, J1.1, and H9/IIIB) and their uninfected parental cell line (A3.01, Jurkat, and H9). RT reaction was carried with or without AST-tag RT primer, and with or without RT enzyme. Only the +/+ combination is shown. Panel C: Quantification of ASP RNA expression in resting CD4+ T cells from two uninfected donors (Controls A and B) and three infected patients under suppressive antiretroviral therapy for > 24 months (Patients A, B and C). RT reaction was carried with or without AST-tag RT primer, and with or without RT enzyme. Only the +/+ combination is shown. Graphs report average and standard deviation calculated from three replicate samples. ND: not detected.
