Abstract
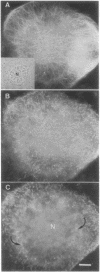
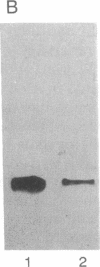
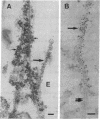
Incorporation of Paramecium axonemal tubulin into lysed endosperm cells of the higher plant Haemanthus enabled us to identify sites of microtubule assembly. This exogenous Paramecium tubulin could be traced by specific antibodies that do not stain endogenous plant microtubules. Intracellular copolymerization of protozoan and higher plant tubulins gave rise to hybrid polymers that were visualized by immunofluorescence and by immunoelectron microscopy. The addition of exogenous tubulin revealed many free ends of endogenous microtubules that were competent to assemble ciliate tubulin. The functional roles of the nuclear surface and the equatorial region of the phragmoplast as plant microtubule-organizing centers, which were revealed by the intense incorporation of exogenous tubulin, are discussed. These data shed light on the present debate on higher plant microtubule organizing centers.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adoutte A., Claisse M., Maunoury R., Beisson J. Tubulin evolution: ciliate-specific epitopes are conserved in the ciliary tubulin of Metazoa. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):220–229. doi: 10.1007/BF02099751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajer A. S., Molè-Bajer J. Asters, poles, and transport properties within spindlelike microtubule arrays. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):263–283. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajer A. S., Molè-Bajer J. Reorganization of microtubules in endosperm cells and cell fragments of the higher plant Haemanthus in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):263–281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calarco-Gillam P. D., Siebert M. C., Hubble R., Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Centrosome development in early mouse embryos as defined by an autoantibody against pericentriolar material. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton L., Black C. M., Lloyd C. W. Microtubule nucleating sites in higher plant cells identified by an auto-antibody against pericentriolar material. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):319–324. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J., Lambert A. M., Bajer A. S., Moeremans M., De Brabander M. Visualization of microtubules in interphase and mitotic plant cells of Haemanthus endosperm with the immuno-gold staining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1898–1902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., Jackson W. T., McIntosh J. R. Polarity of spindle microtubules in Haemanthus endosperm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):644–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuens G., Hill A. M., Levilliers N., Adoutte A., DeBrabander M. Microtubule dynamics investigated by microinjection of Paramecium axonemal tubulin: lack of nucleation but proximal assembly of microtubules at the kinetochore during prometaphase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):939–953. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., Jackson W. T. Microtubules and early stages of cell-plate formation in the endosperm of Haemanthus katherinae Baker. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):437–446. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., Wolniak S. M. Membranes in the mitotic apparatus: their structure and function. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;90:169–238. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61490-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Evans L., Schulze E., Kirschner M. Sites of microtubule assembly and disassembly in the mitotic spindle. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Microtubule assembly nucleated by isolated centrosomes. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):232–237. doi: 10.1038/312232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott A. R., Foster K. E., Warn R. M., Gull K. Incorporation of tubulin from an evolutionarily diverse source, Physarum polycephalum, into the microtubules of a mammalian cell. J Cell Sci. 1989 Apr;92(Pt 4):595–605. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozdzial M. M., Haimo L. T. Reactivated melanophore motility: differential regulation and nucleotide requirements of bidirectional pigment granule transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2755–2764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmit A. C., Lambert A. M. Microinjected fluorescent phalloidin in vivo reveals the F-actin dynamics and assembly in higher plant mitotic cells. Plant Cell. 1990 Feb;2(2):129–138. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmit A. C., Lambert A. M. Plant actin filament and microtubule interactions during anaphase--telophase transition: effects of antagonist drugs. Biol Cell. 1988;64(3):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(88)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltys B. J., Borisy G. G. Polymerization of tubulin in vivo: direct evidence for assembly onto microtubule ends and from centrosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1682–1689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantard M., Lambert A. M., De Mey J., Picquot P., Van Eldik L. J. Characterization and immunocytochemical distribution of calmodulin in higher plant endosperm cells: localization in the mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):488–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., O'Brien E. T., Pryer N. K., Soboeiro M. F., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P., Salmon E. D. Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: rate constants and transition frequencies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1437–1448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick S. M. Immunofluorescence microscopy of tubulin and microtubule arrays in plant cells. III. Transition between mitotic/cytokinetic and interphase microtubule arrays. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1985 Apr;9(4):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(85)90031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]