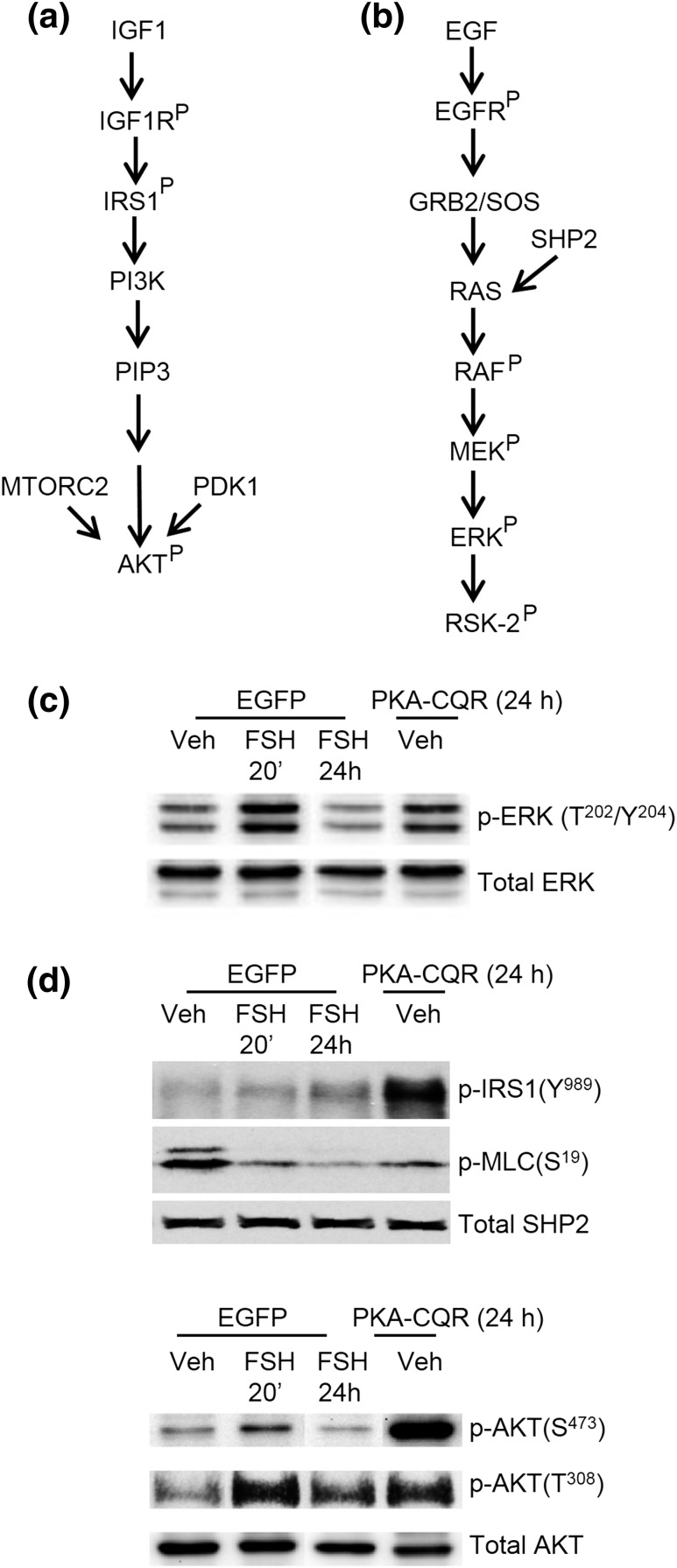
Figure 1.
Canonical signaling to ERK and PI3K, and PKA signaling in GCs. (a, b) Canonical signaling pathways by which IGF-1 signals to activate PI3K to promote phosphorylation/activation of AKT and EGF signals to promote the phosphorylation/activation of ERK, respectively. AKT phosphorylation targets regulate translation, transcription, metabolism, cell survival, and angiogenesis [reviewed in (38)]; ERK phosphorylation targets regulate transcription, translation, and metabolism [reviewed in (42, 43)]. (c, d) The ability of constitutively active PKA catalytic subunit mutant (PKA-CQR) to promote phosphorylation of IRS1(Tyr989) [modified from (32)] and AKT (Thr308, Ser473) [modified from (31)] and activation of PP1 to dephosphorylate myosin light chain (Ser19) [modified from (32)] to activate PI3K/AKT, and phosphorylation of ERK (Thr202/Tyr204) to activate MAPK/ERK signaling [modified from (31)]. Preantral GCs were transduced with enhanced green fluorescent protein or PKA-CQR for 24 hours, then treated with vehicle (Veh) or FSH, as indicated. Treatment of GCs with FSH for 20 minutes generally yields a maximal phosphorylation response that declines thereafter; however, expression of the PKA-CQR lentivirus recombinant protein required 24 hours to detect consistent protein phosphorylation (31). Thus, the 24-hour stimulation window reflects the initial responses of GCs to active PKA. PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; MTORC2, mammalian target of rapamycin 2.