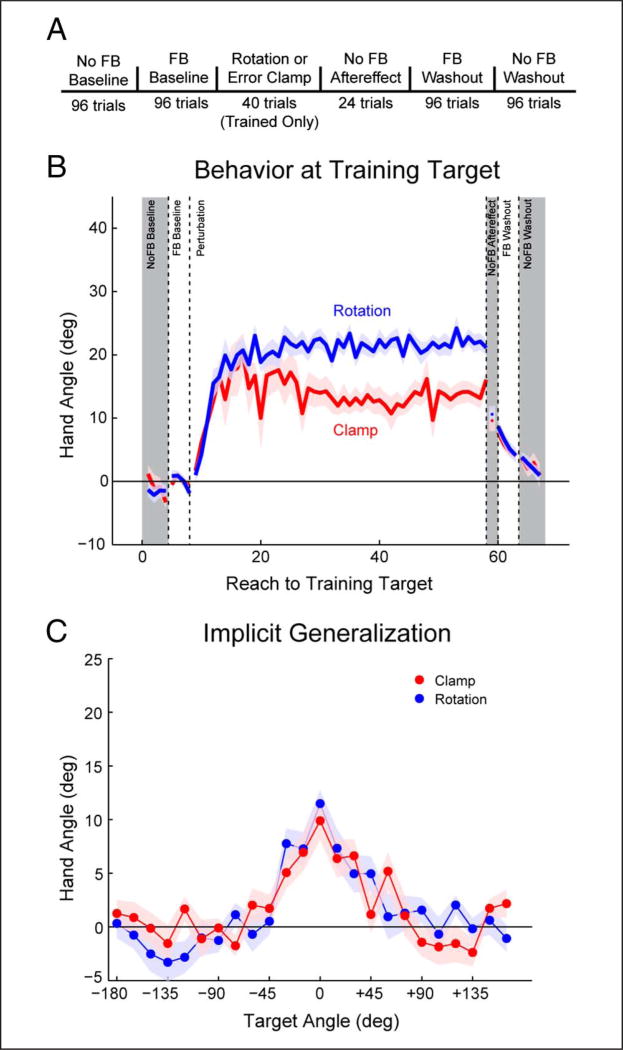
Figure 2.
Aftereffects and generalization are similar following exposure to a standard visuomotor rotation and a clamped visual feedback. (A) Task trial design. Participants reached to all targets for every phase of the experiment, except for the perturbation block in which all reaches were to a single target. (B) Behavior at the training target during each phase of the experiment. Both groups show a change in heading angle in response to the visual feedback perturbation, with the rotation group changing hand angle by an additional 8°. However, there was no difference once the perturbation was removed. (C) Baseline subtracted aftereffect at all targets. The generalization functions are remarkably similar for the two groups around the workspace. Values are group means; shading and error bars denote SEM. Gray shading denotes cycles without visual feedback.