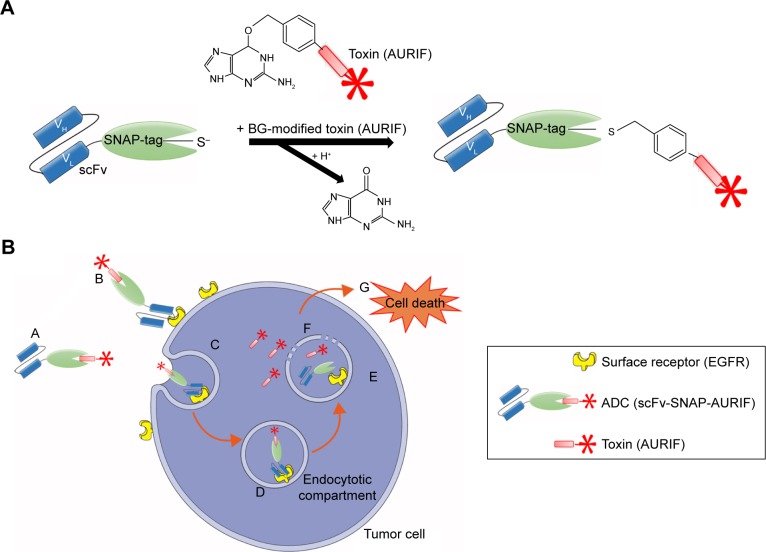
Figure 1.
SNAP-tag technology and the mechanism of action of the scFv-SNAP-AURIF ADCs.
Notes: SNAP-tag technology allows site-specific covalent and irreversible coupling of BG-modified cytotoxic payloads such as AURIF to scFv-SNAP fusion proteins. (A) The SNAP-tag undergoes a self-labeling reaction to form a covalent bond with BG derivatives. (B) (A and B) The scFv-SNAP-AURIF ADC binds via its scFv specifically to the extracellular receptor of the target tumor cell and (C and D) is internalized receptor mediated into the lysosomal compartment. (E and F) Due to acidification and enzymatic reactions within the lysosomes, the fusion protein is degraded and the toxin (AURIF) is set free into the cytosol. (G) Auristatin-based toxins have an effect on the microtubule structure and cause cell death by apoptosis.
Abbreviations: ADC, antibody–drug conjugate; BG, benzylguanine; AURIF, auristatin F; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; scFv, single-chain fragment variable; VH, heavy chain variable domain; VL, light chain variable domain.