Figure 3.
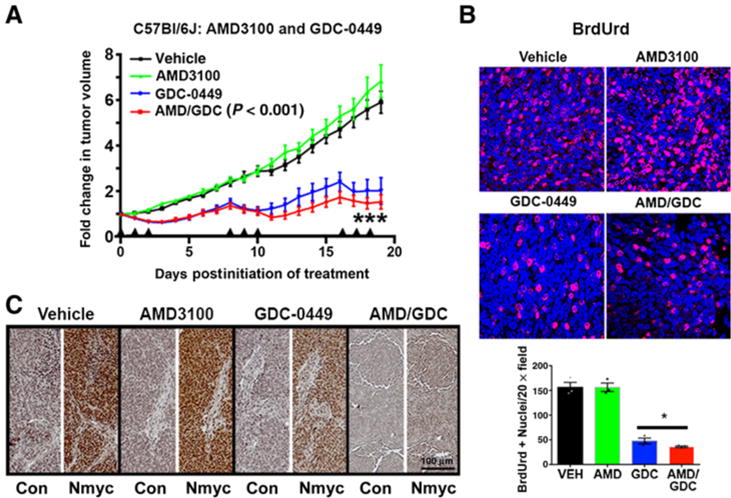
Combined Smo and CXCR4 antagonism is more efficacious than Smo antagonism alone against SmoA1 medulloblastoma. A, Primary SmoA1 tumor cell isolates (n = 5 tumors) were used to generate five cohorts of 20 to 25 immunocompetent C57Bl/6J mice bearing subcutaneous tumor implants. Mice from each cohort were separated into four treatment groups yielding final treatment numbers of vehicle (VEH; n = 19), AMD3100 (n = 21), GDC-0449 (n = 21), and AMD3100/GDC-0449 (n = 23). Mice were treated with the indicated drug for 3 consecutive days (arrowheads), followed by 5 days of no treatment. This dosage schedule was repeated for a total of three treatment periods prior to tumor harvest. Tumors were measured daily, blinded to treatment group, using digital calipers in three dimensions (width, height, and length), and all measurements were normalized to the tumor size at day 0 (pretreatment). ***, P < 0.001 comparing GDC-0449–treated tumors and AMD3100/GDC-0449–treated tumors, two-way ANOVA. B, Representative images of BrdUrd labeling (red) in each of the treatment groups. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. BrdUrd-positive and total nuclei were counted in sections from three separate mice from each treatment group. Quantification of the mean and SEM of the numbers of positive nuclei per high powered fields are shown. Both GDC-0449 and AMD3100/GDC-0449 treatments significantly reduced the numbers of BrdUrd-positive nuclei. The combined treatment suppressed BrdUrd incorporation more than GDC alone (*, P < 0.05, as determined by two-tailed t test). C, Representative images of Nmyc or no primary control (Con) immunostaining from each of the treatment groups. Scale bar, 100 μm.
