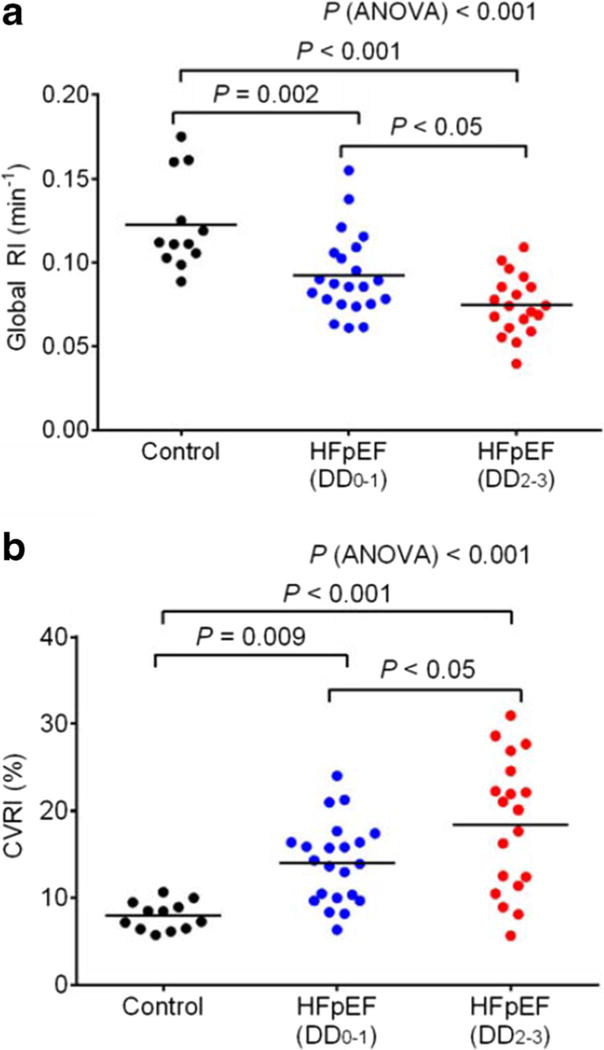
Fig. 4.
a Global retention index of11 C-hydroxyephedrine determined from dynamic PET imaging in control subjects (n = 12) and patients with heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF) that have normal to mild diastolic dysfunction (DD0–1; n = 22) and moderate to severe diastolic dysfunction (DD2–3; n= 19). b Tracer uptake heterogeneity determined by the coefficient of variation in 11C-hydroxyephedrine retention indices (RI/min) between left ventricular segments (17-segment model) in control subjects (n = 12) and in HFpEF patients with normal to mild diastolic dysfunction (DD0–1; n = 22) and moderate to severe diastolic dysfunction (DD2–3; n = 19). Global retention index and tracer uptake heterogeneity were significantly different between controls and HFpEF patients and between HFpEF patients with normal to mild diastolic dysfunction and moderate to severe diastolic dysfunction. RI/min global retention index per minute, HFpEF heart failure with persevered ejection fraction, DD diastolic dysfunction, 0 no diastolic dysfunction, 1 mild diastolic dysfunction, 2 moderate diastolic dysfunction, 3 severe diastolic dysfunction, CVRI% coefficient of variance in global retention index per minute among left ventricular segments (this research was originally published in JNM [79••])