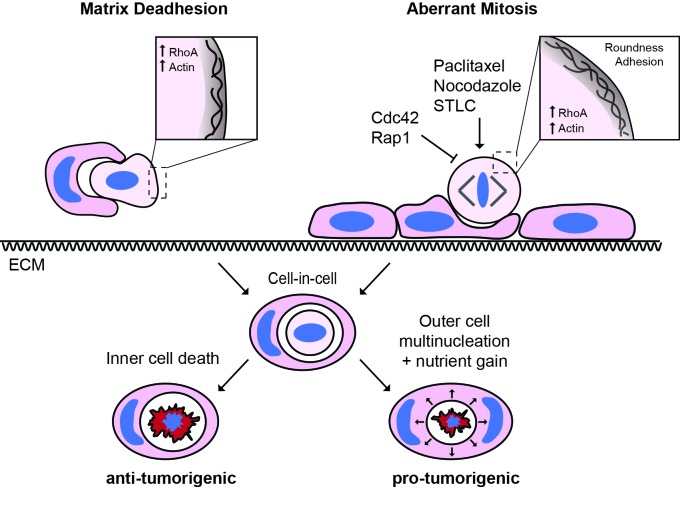
Figure 8. The triggers and consequences of entosis in cancer.
Entosis can be triggered among epithelial cells through either matrix deadhesion or aberrant mitosis. Mitotic entosis is associated with enhanced deadhesion and rounding during cell division, which can be induced by inhibition of Cdc42 or Rap1, or through prometaphase arrest. RhoA activity is important in both suspension and mitosis-induced entosis, driving ROCK-dependent myosin activation. Regardless of the triggering mechanism, entosis promotes both inner cell death and outer cell nutrient gain and multi-nucleation, with the potential to confer both anti- and pro-tumorigenic effects.