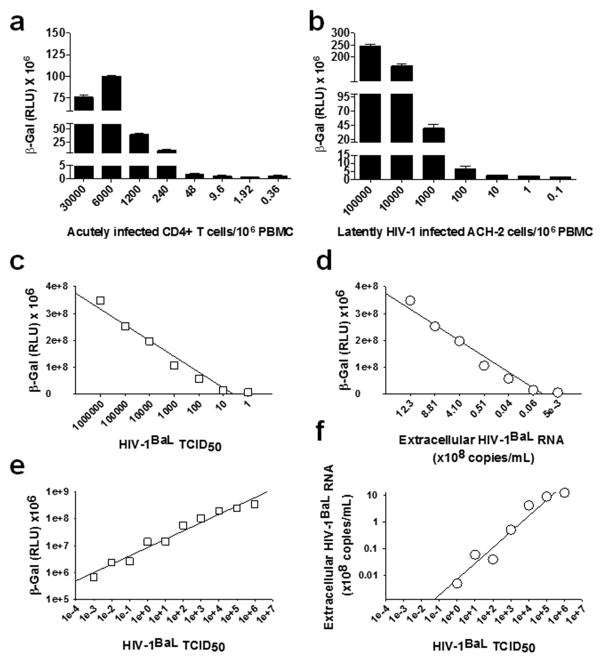
Fig. 1. Sensitivity of TZM-bl cells to replication competent HIV-1.
a) Acutely infected HIV-1BaL-positive CD4+ T lymphocytes (30% infection frequency as determined by flow cytometry of intracellular p24) were serially diluted with uninfected CD8+ T cell- PBMC. 1×105 cells from each serial dilution were added to 5×104 TZM-bl cells in a 96-well plate. β-gal activity was measured by chemiluminesence 48 h later. The relative light units (RLU) for the control (460,000 +/− 56,000) were subtracted from each assay sample. b) Latently HIV-1 infected ACH-2 cells were treated with 100nM PMA, serially diluted with uninfected CD8+ T cell-depleted PBMC, and added to TZM-bl cells, as described above. c) Correlation between the TCID50 for HIV-1BaL and β-gal activity in the TZM-bl cells. TZM-bl cells were infected with HIV-1BaL and β-gal activity was measured 48 h later. d) Correlation between the β-gal activity for HIV-1BaL 48 h post infection and virus production (assessed by extracellular virion associated HIV-1 RNA 10 days post-infection) e) Detection of β-gal activity in the TZM-bl cells as a function of HIV-1BaL TCID50. We observed a linear relationship between β-gal activity and TCID50 down to a TCID50 of 0.001. f) Detection of extracellular virion-associated RNA as a function of HIV-1BaL TCID50. We observed a linear relationship between extracellular virion-associated RNA and TCID50 down to a TCID50 of 1. P values (cited in the text) for c, d, e and f were obtained using the Pearson test.