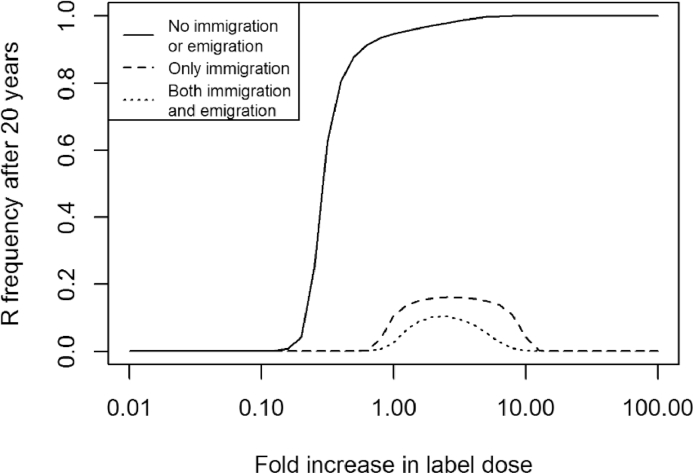
Fig. 5.
Immigration is an important factor determining whether high doses suppress the selection of resistance. Here the resistance frequency is shown after 20 years of application with a range of doses from 1% of a label dose to 100x a label dose in a diploid sexually reproducing population with default parameters (see Table 1). Three versions of movement between the untreated and treated populations are shown: no immigration or emigration (), solid line; immigration from the untreated population into the treated population (), but no emigration (), dashed line; and both immigration () and emigration (), dotted line.