Figure 3.
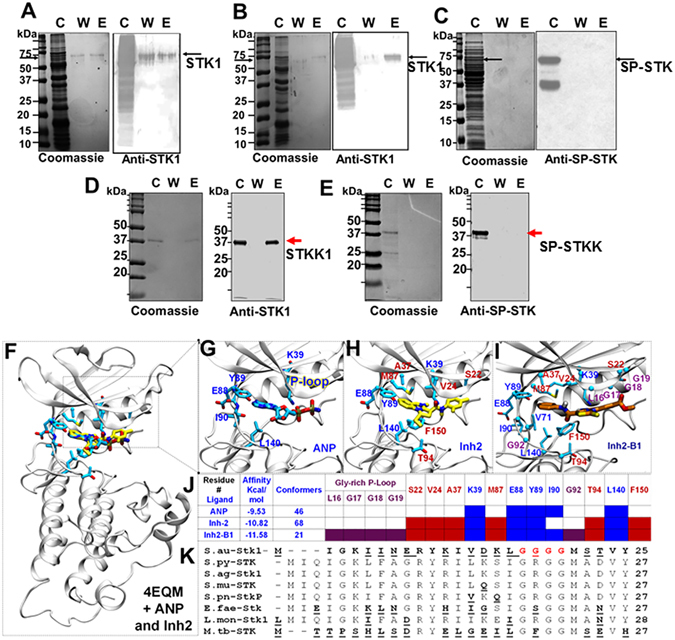
Binding of Inh2 and Inh2-B1 to the catalytic ATP-binding pocket of STK1. In vivo binding of (A) Inh2 and (B) Inh2-B1 to S. aureus STK1 as determined by ATP-column chromatography. Whole cell lysostaphin-digest of the MW2-wild type strain was passed on to the buffered equilibrated ATP-agarose column and eluted with 50 µM Inh2 or Inh2-B1 followed by detection of STK1 in Western Blot assay using the anti-STK1 polyclonal antibody as described in the Materials and Methods section. (C) A similar experiment with whole cell lysate of the phage-lysin digested S. pyogenes M1T1 strain revealing no elution of SP-STK. STK1 (~90 kDa) and SP-STK (~70 kDa) proteins (see pointed arrow) in their respective bacterial lysates are found without/ with its degraded forms as described previously20, 36. C-cell lysate, W-wash fraction, E- elution fraction. (D) Binding of the purified recombinant STKK1 to solid-phase ATP- column and its elution by Inh2-B1. (E) Binding of the purified recombinant SP-STK to solid-phase ATP- column and its elution by Inh2-B1. (F) In silico, molecular docking analysis-based the highest scored docked pose of ANP and Inh2 in the binding pocket of the kinase domain of S. aureus STK1 (PDB ID 4EQM). The protein is shown in the white cartoon. Interaction of (G) ANP (inactivated ATP shown in cyan), (H) small molecule compound Inh2 (shown in yellow) and (I) Inh2-B1 (shown in dark orange) and key residues (only the side-chain non-hydrogenous atoms) around 3.5 Å from the inhibitor are shown in the sticks. The coloring code of the atom type: C (Yellow or green in inhibitors and cyan in ANP), N (blue), and O (red). (J) A summary table is showing the association of ANP, Inh2, and Inh2-B1 with amino acid residues reflecting their affinity for the ATP-binding pocket and a number of conformers clustered in this region during molecular docking analysis. ANP constitutes key residues (blue fonts). The residues around Inh-2 are shown in red fonts and the residues around P-loop that directly interact with Inh2-B1 are shown in purple fonts (See also Fig. S5 for affinity and number of conformers for all Inh2 derivatives). (K) A comparison of the N-terminal sequence of STK1 with those of other Gram-positive pathogens showing the unique nature of the S. aureus STK1 P-loop (Red fonts). The underlined bold letters denote non-conserved amino acid residues.
