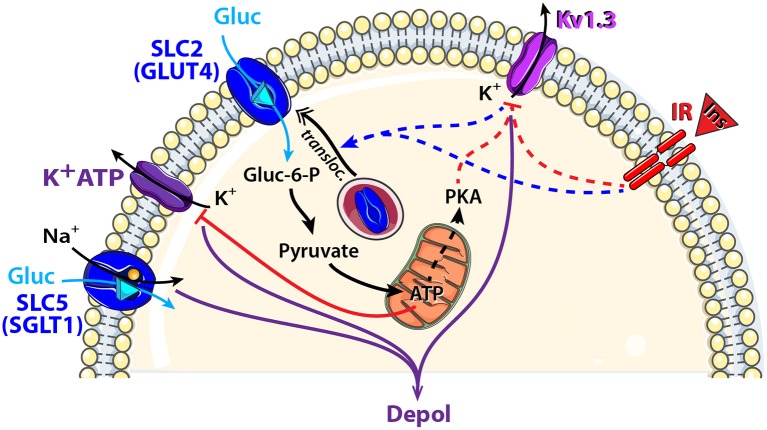
Figure 3.
Schematic model showing glucose sensing signaling pathways that might modulate neuronal activity of central olfactory areas. Two types of glucose transporters and their associated downstream cellular processes are observed in central olfactory areas. SGLT1, located in the OB, is electrogenic and combines glucose (Gluc: blue triangle) translocation with an influx of Na+. GLUT4, located mainly in the OB and PC, is non-electrogenic and is associated with the insulin pathway. Indeed, insulin (Ins, red triangle) binding to its receptor (IR: insulin receptor) depolarizes MCs through Kv1.3 channel closure and induces GLUT4 translocation to the membrane. Glucose intake increases as well as the mitochondrial production of ATP and the cytosolic protein kinase A (PKA). Activation: blue arrow, inhibition: red line. Direct and indirect action of one molecule: full and dotted line respectively.