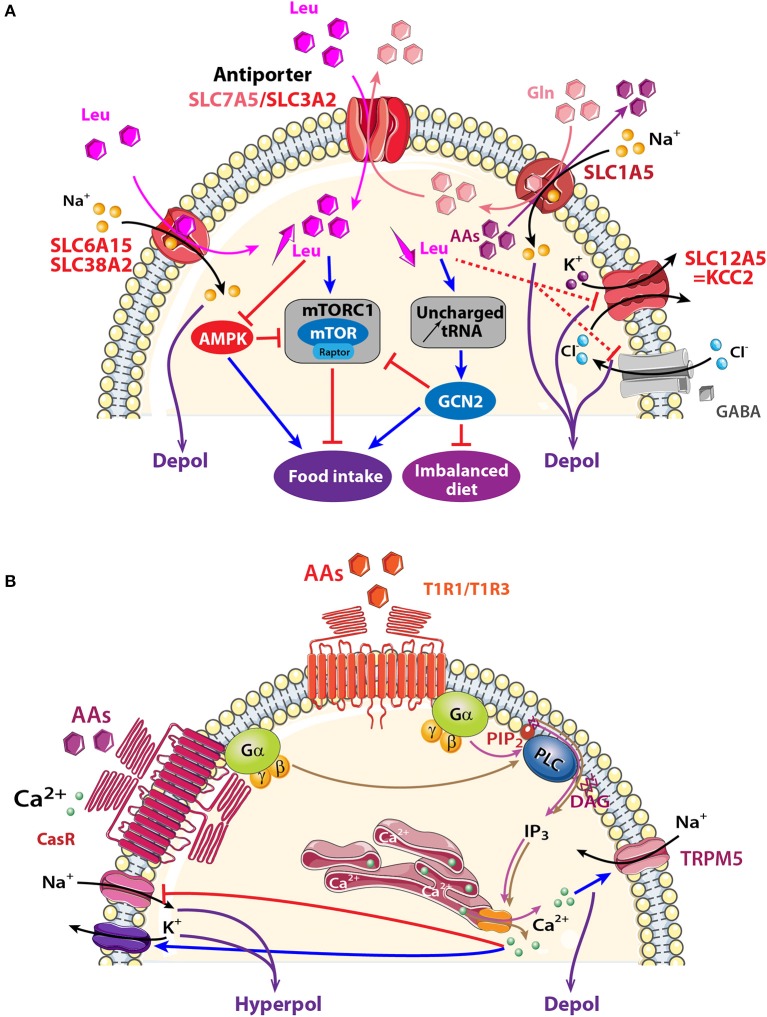
Figure 4.
Schematic model showing AA sensing signaling pathways that might modulate neuronal activity of central olfactory areas. (A) Three electrogenic transporters (SLC6A15, SLC38A2, and SLC1A5) and one non-electrogenic antiporter SLC7A5/SLC3A2 are observed in the OB and the PC. AAs fluxes depend on physiological needs, on the importance of transported AAs (essential or non-essential), and on the cellular gradient of AAs. When leucine (Leu) and glutamine (Gln) are highly available, they are co-transported with sodium inside the cell through SLC6A15, SLC38A2 or SLC1A5. Intracellular Gln is in turn co-exchanged with Leu via the bidirectional antiporter SLC7A5/SLC3A2. The anterior PC (APC) detects essential AA deficiency that increases uncharged tRNA and activates the general amino acid control non-derepressible 2 (GCN2) pathway. The concomitant down regulation of GABAA receptor and KCC2 transporter disinhibits the APC that send messages to nutritional brain areas in order to stop eating the imbalanced diet. Signaling proteins of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex1 (mTORC1) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways are also present in olfactory areas, which suggests that these structures could also be implicated in detecting AA abundancy or scarcity and indirectly modulating food intake. (B) Two AA receptors are described: T1R1/T1R3, and CasR receptors. Both are G-protein-coupled receptors and AA binding activates heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins composed of α-gustducin (Gα) and Gβγ subunits (brown and pink arrows). Gαpromotes phosphatidylinositol phosphate 2 (PIP2) activation of phospholipase C (PLC), leading to the production of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (D). IP3 opens ion channels on the endoplasmic reticulum, releasing Ca2+ into the cytosol of cells. Depending on the specific ion channels present on the membrane, a cell could be depolarized after melastatin-related transient receptor potential (TRPM5) channel opening or could be hyperpolarized after Na+ channel closure (red line) or Ca2+-dependent-K+ channel opening (blue arrow). AAs: hexagons; activation: blue arrow, inhibition: red line. Direct and indirect action of one molecule: full and dotted line respectively.