Figure 3.
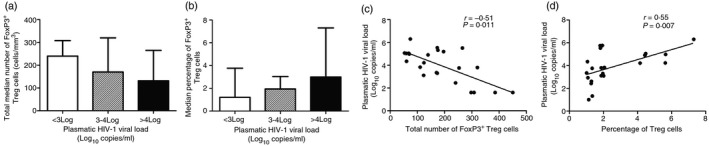
HIV infection modulates regulatory T (Treg) cell frequencies and numbers. HIV‐infected participants were divided into three groups according to their plasmatic HIV viral loads [VL< 3 Log copies/ml (n = 8); 3–4 (n = 8); > 4 (n = 12)]. The total number of Treg cells decreased when the plasmatic HIV viral load increased (a), whereas an inverse tendency was observed when Treg cell frequencies were considered (b) although the differences were not significant using Kruskal–Wallis test. However, plasmatic HIV viral load correlated negatively with total Treg cell numbers (r = −0·51; P = 0·011; c) and positively with Treg cell frequencies (r = 0·55; P = 0·007; d) using Spearman test.
