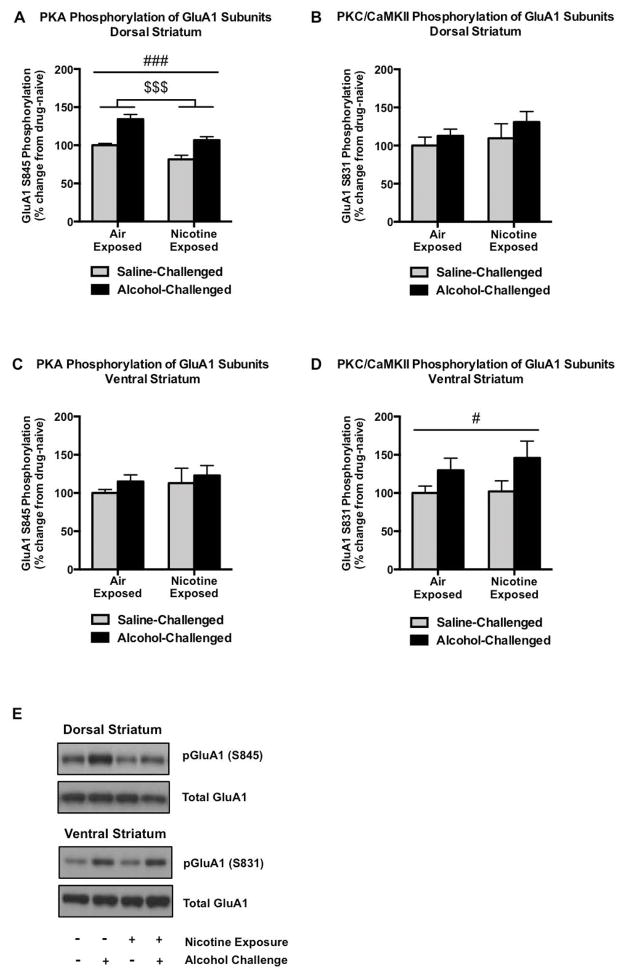
Figure 3.
GluA1 phosphorylation in the striatum. Alcohol significantly increases PKA-mediated GluA1 phosphorylation in the dorsal striatum in both air- and nicotine-exposed groups, while chronic intermittent nicotine exposure and withdrawal decreases pGluA1S845 (A). Neither of these effects was observed with regard to PKC/CaMKII-mediated protein phosphorylation of GluA1 subunits (B). In contrast to the other regions investigated, alcohol failed to alter PKA-mediated phosphorylation of GluA1 in the ventral striatum (C), although it significantly increased PKC/CaMKII-regulated GluA1 phosphorylation (D). Representative pGluA1S845, pGluA1S831, and total GluA1 immunoblots are indicated in (E). N=6/group. Pound and dollar signs indicate a main group effect of alcohol treatment (#p<0.05, ###p<0.001) or nicotine exposure ($$p<0.01), respectively.