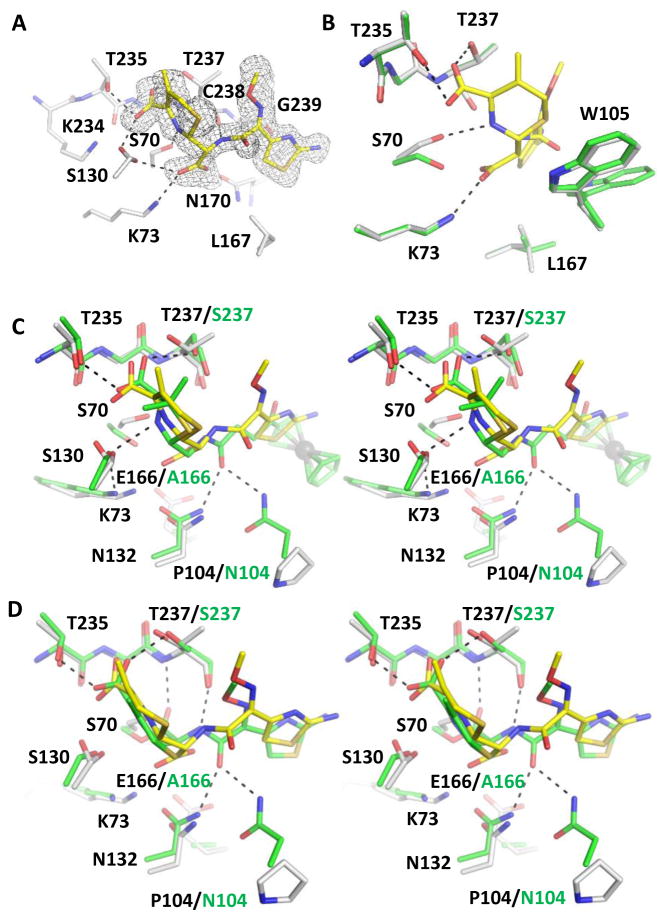
Figure 2.
KPC-2 cefotaxime product complex. The protein and ligand of the complex are shown in white and yellow, respectively. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines. (A) The unbiased Fo-Fc electron density map (gray) of hydrolyzed cefotaxime contoured to 2σ. (B) Superimposition of KPC-2 product complex onto apo-protein (green) with details showing the interactions involving Ser70, Lys73, the cefotaxime ring nitrogen, and the newly formed C8 carboxylate group. PyMOL alignment RMSD = 0.153 Å over 272 residues. (C) Superimposition of KPC-2 product complex and CTX-M-14 E166A penilloate product complex with a ruthenocene-conjugated penicillin (green, with residues unique to CTX-M-14 E166A labeled in green), in stereo view. The ruthenium atom is shown as a gray sphere. PyMOL alignment RMSD = 0.617 Å over 272 residues. (D) Superimposition of KPC-2 product complex with Toho-1 E166A acyl-enzyme complex with cefotaxime (green, with residues unique to Toho-1 E166A labeled in green). PyMOL alignment RMSD = 0.602 Å over 264 residues.