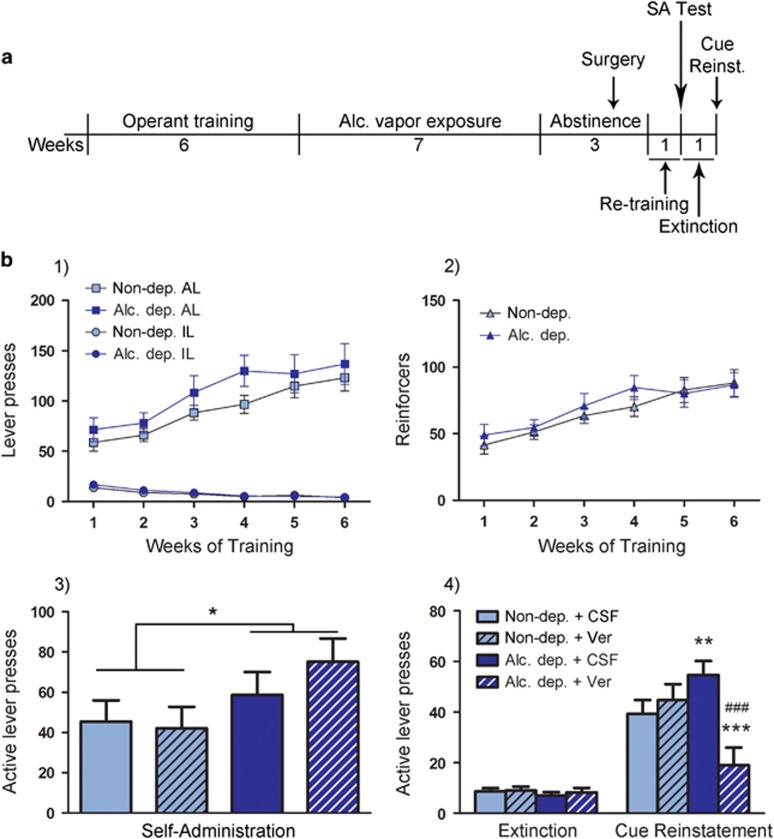
Figure 4.
LTCC antagonist verapamil i.c.v. administration blocks cue-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking in alcohol-dependent but not control rats, with no effect on alcohol self-administration. (a) Experimental outline: rats were trained to self-administer alcohol, and vapor or air exposed. During the following abstinence, guide cannulas for i.c.v. injections were implanted. After recovery rats were retrained, then tested for self-administration (SA) following i.c.v. injection of verapamil (Ver, 120 μg/5 μl) or vehicle (aCSF, 5 μl). This was followed by 1 week of extinction, after which cue-induced reinstatement was tested following i.c.v. injection of verapamil (120 μg/5 μl) or aCSF (5 μl). For details, see Materials and Methods. (b) (1) Graph shows lever presses during 6 weeks of self-administration training, with active lever (AL) presses steadily increasing and inactive lever presses (IL) at an expected low level. (2) As AL presses were followed by a 3 s timeout period during which additional lever presses did not result in alcohol delivery, rats received less reinforcers, as shown here. Neither AL and IL presses nor number of reinforcers differ between control and alcohol-dependent groups. (3) Self-administration following i.c.v. administration of verapamil or aCSF. Two-way ANOVA showed a significant overall effect on increased AL presses in dependent compared with nondependent rats (*p<0.05). Verapamil did not result in significant differences between groups. N=7/group for non-dep. aCSF, non-dep. verapamil, and alc. dep. aCSF, and IL presses (not shown) were below 10 for all groups (range: 3.57–6.66 IL presses). N=6/group for alc. dep. verapamil. (4) Cue-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking following i.c.v. injection of verapamil was blocked in alcohol dependent rats. All other groups show significant reinstatement compared with extinction, and alcohol-dependent rats receiving aCSF show significantly higher reinstatement than control rats receiving aCSF. IL (not shown) were below 10 for all groups (range: 1.42–2.27 IL presses in extinction, 3.5–6.8 IL presses in cue-induced reinstatement). Statistical analysis was performed by repeated measures ANOVA, followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc test, where appropriate, p-values: **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 alc.-dep. vs control; ###p<0.001 verapamil vs CSF. N=8/group for non-dep. aCSF and alc. dep. aCSF, N=6/group for non-dep. verapamil, and N=5/group for alc. dep. verapamil. Alc., alcohol; Alc. dep., alcohol dependent; Non-dep., nondependent.