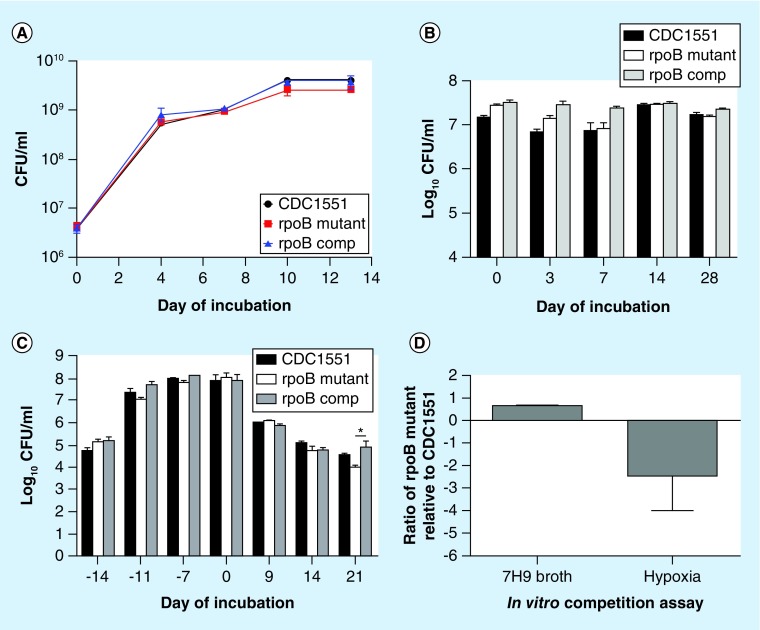
Figure 1. . In vitro phenotypes associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis RpoB mutation H526D.
(A) Growth kinetics of each strain in supplemented Middlebrook 7H9 broth. (B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival during nutrient starvation. (C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival during progressive hypoxia. (D) In vitro competition assay. The rpoB mutant and the wild-type CDC1551 were equally mixed and incubated in supplemented Middlebrook 7H9 broth as well as in the progressive hypoxia model. CFU were counted on 7H10 agar plates with and without 1 μg/ml of Rifampicin on days 0 and 7. The competitive fitness, W of the rpoB mutant relative to the wild-type strain was calculated using the following formula: W = ln (RF/RI)/ln (SF/SI), where RI and SI refer to the number of Rifampicin-resistant and -susceptible bacteria at baseline, respectively, and RF and SF refer to the same bacterial populations at the study end points.
comp: Complemented strain of the RpoB H526D mutant.