Figure 1.
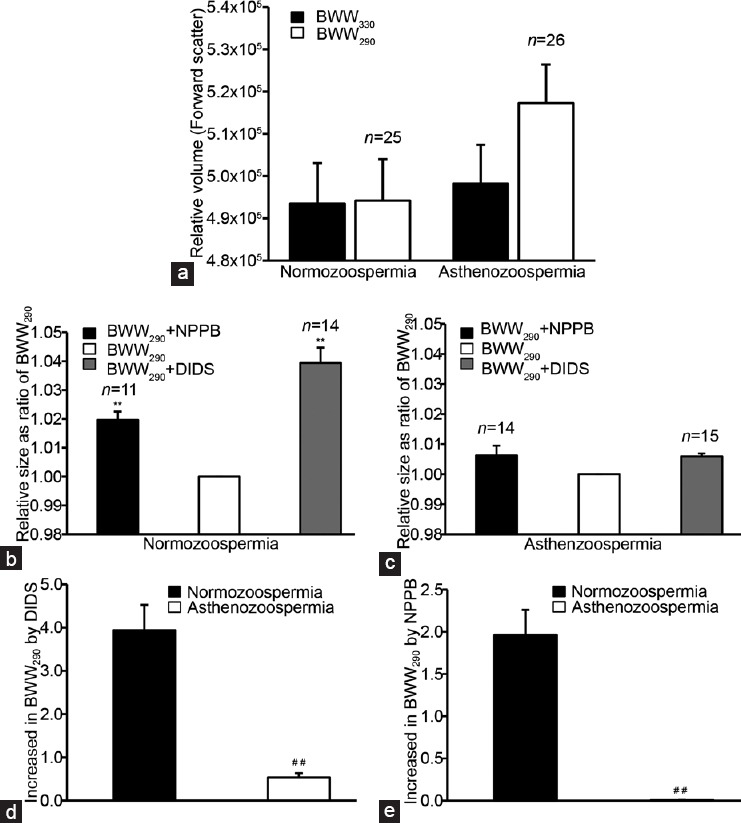
Effects of hypotonic stimulation and the chloride channel blockers NPPB and DIDS on the volumes of spermatozoa from normozoospermic and asthenozoospermic semen samples. Sperm volume was detected by monitoring the forward scatter signals (FSCs) using flow cytometry. (a) Relative sperm volumes expressed as FSC signals of the in the hypotonic (BWW290) and isotonic (BWW330) solutions; (b) and (c) the effects of NPPB and DIDS (both at 100 μmol l−1) on the relative sperm volume (expressed as the FSC signal ratio of blockers/BWW290 control) in the normozoospermic and asthenozoospermic semen samples, respectively; and the percentage sperm volume increases caused by (d) DIDS and (e) NPPB in the hypotonic solution, respectively. **P < 0.01, BWW290 and channel blockers vs BWW330; ##P < 0.01, asthenozoospermia vs normozoospermia. Data are shown as the mean ± s.e. (semen samples, n from 11 to 26). s.e.: standard error; DIDS: 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; NPPB: 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino) benzoic acid; BWW: Biggers, Whitten and Whittingham.
