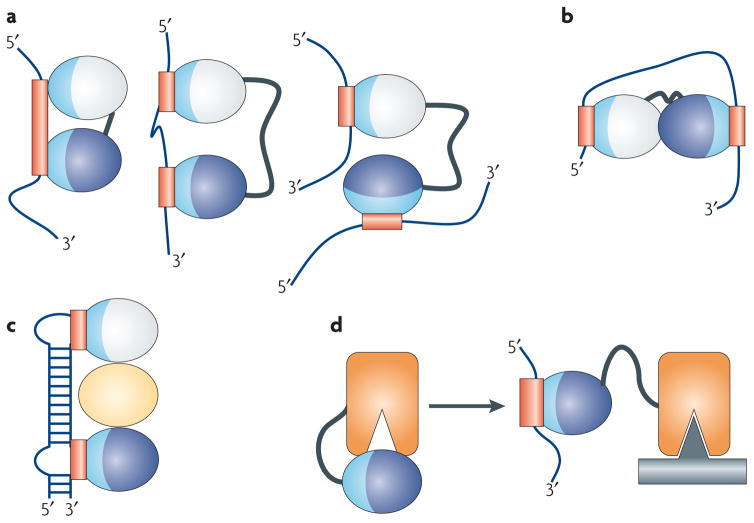
Figure 2. RNA-binding modules are combined to perform multiple functional roles.
RNA-binding domains function in a variety of ways. (a) They recognize RNA sequences with a specificity and affinity that would not be possible through a single domain or if multiple domains did not cooperate. Multiple domains combine to recognize a longer RNA sequence (left), sequences separated by many nucleotides (centre), or RNAs belonging to different molecules altogether (right). (b) RNA-binding domains can organize mRNAs topologically by interacting simultaneously with multiple RNA sequences or (c) they can function as spacers to properly position other modules for recognition. (d) They can combine with enzymatic domains to define the substrate specificity for catalysis or regulate enzymatic activity. In this figure, the RNA-binding modules are represented as ellipses with their RNA-binding surfaces colored in light blue, with the corresponding binding sites within the RNA colored in red; individual domains are colored differently.