Fig. 2.
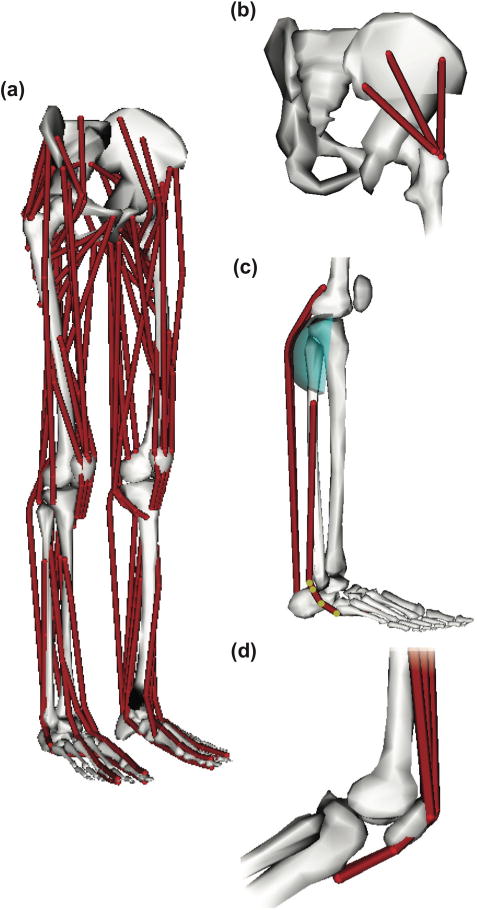
Muscles were modeled as massless linear actuators. (a) The model included 80 muscle-tendon units (40 per leg) actuating the lower limbs. (b) Muscles with broad attachment areas (e.g., gluteus medius) were modeled using multiple independent muscle-tendon units. (c) Muscle geometry was modeled using a set of body-fixed points (highlighted) and wrapping surfaces. (d) The force transmission mechanism between the quadriceps and patellar ligament was modeled implicitly by wrapping the quadriceps muscles over the patella and inserting the muscles directly to the tibia.
