Figure 3. Dependence of DNA-protein crosslinking on oligonucleotide structure and oxidant type.
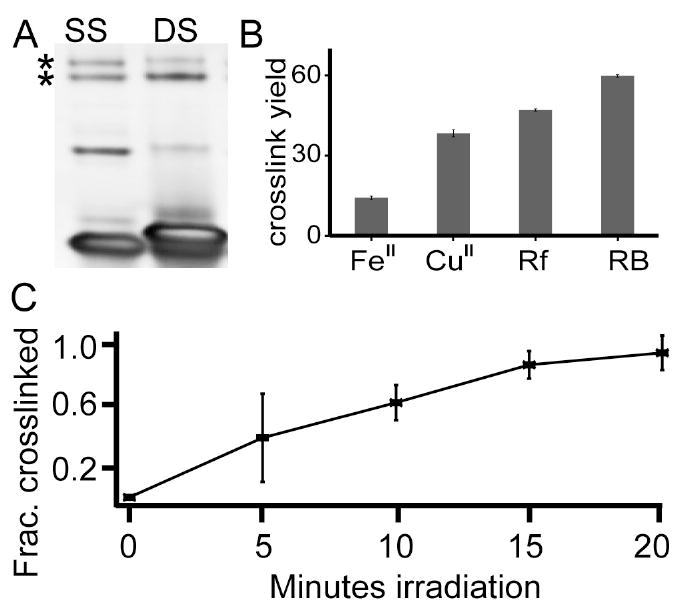
(A) The degree of oxidative crosslinking with a single stranded DNA, SS, is compared with that of double stranded, DS, DNA. The two DNA structures have a comparable tendency to form DNA-protein crosslinks. (B) Four different oxidant systems were used to generate crosslinks at equimolar concentrations of protein to DNA. Fe(II)-H2O2, Cu(II)-H2O2, riboflavin and rose bengal oxidation systems all generated high yields of crosslink despite the divergent oxidation mechanisms. Error bars are standard deviations with n=3. (C) Rose bengal induced crosslinks occur rapidly and linearly increase with irradiation time within the first twenty minutes.
