Figure 6. Guanine is the major crosslink site.
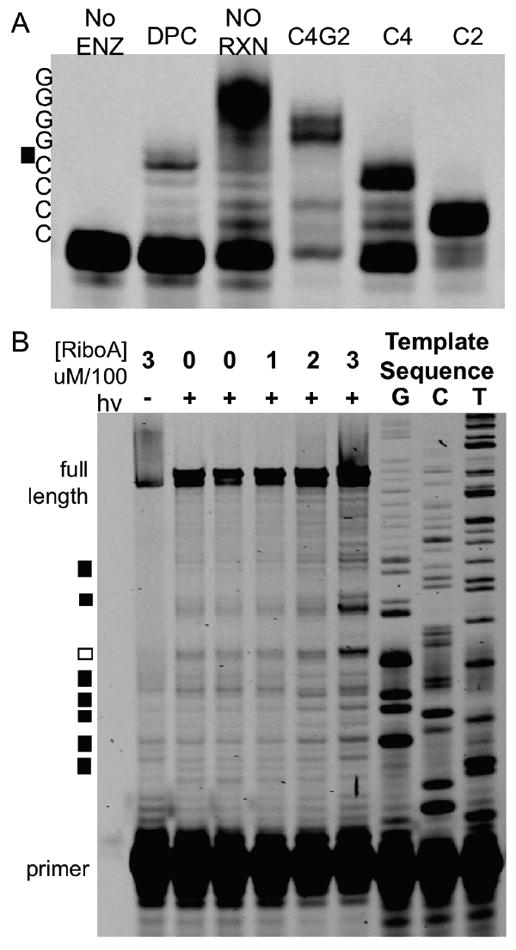
(A) The 27-nucleotide DNA was crosslinked to Ribonuclease A, the product subsequently purified, and annealed to a labeled primer. Isolation and extension of a no reaction control (lane NO RXN) led to full extension when compared to the truncated sequences on the right lanes (C4G2, C4, C2). C4G2 lacks the last two guanosine nucleotides from the 5’-end of the 27-mer, while C4 lacks the last 4 guanosine nucleotides and C2 does not have the last six nucleotides. Extension of the crosslinked product resulted in a stop before the poly-G tract (C4G2). (B) A 100-nucleotide mixed sequence DNA, rose bengal, bovine serum albumin, and Ribonuclease A at the listed concentrations (top) were incubated. Lack of irradiation or Ribonuclease A led to extension predominantly to the full-length product. As the Ribonuclease A concentration increases, new, shorter molecular weight bands are observed. Boxes to the left mark the new bands. Black boxes (7 of 8 new bands) represent crosslinks at guanine. The remaining white box occur two nucleotides before a guanine.
