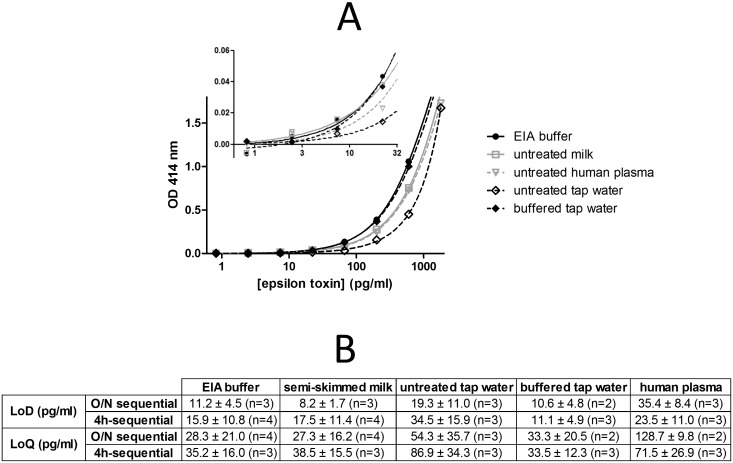
Fig 6. Detection of epsilon toxin spiked in EIA buffer, milk, tap water and human plasma using sequential enzyme immunoassay PεTX7/PεTX6-AChE.
Serial dilutions of epsilon toxin were performed in different matrices: EIA buffer, pure semi-skimmed milk, pure human plasma, untreated pure tap water and buffered tap water. These dilutions were detected using the overnight (A and B) or the 4-h (B) sequential enzyme immunoassay PεTX7/PεTX6-AChE (see Materials and methods). In A, in order to allow a direct comparison, the nonspecific binding was subtracted. The inserts show the low-concentration part of the curve. Error bars represent standard deviations for a duplicate measurement. Theoretical limits of detection (LoD = mean of nonspecific binding + 3 standard deviations) and quantification (LoQ = mean of nonspecific binding + 10 standard deviations) were calculated using GraphPad Prism software with a nonlinear regression model using a two-site binding saturation curve fit (total and nonspecific binding).