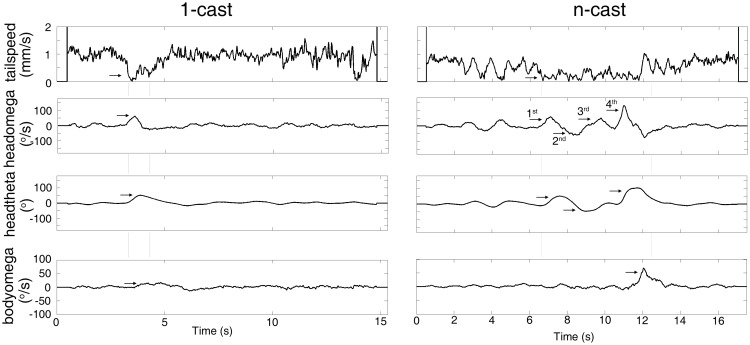
Fig 1. Typical 1-cast and n-cast turns in light-spot based phototaxis.
The tailspeed (top row), headomega (second row), headtheta (third row) and bodyomega (bottom row) time series of a larval 1-cast (left column) and a 4-cast (right column) turning events. Rectangular frames show the stop periods. Arrows in tailspeed point to the onset of the stop period. Arrows in headomega point to headomega peaks indicating head casts following stop. Arrows in headtheta point to the largest body angles. Arrows in bodyomega point to the bodyomega peaks which indicate larval turning. In 1-cast, the larva entered the light spot at 2.87 second. In 4-cast, the larva entered the light spot at 2.0 second, the stop period indicated by the rectangular frame is the second stop period after larva entered light spot.