Figure 3. Primary cilium proteins implicated in skeletal dysplasias.
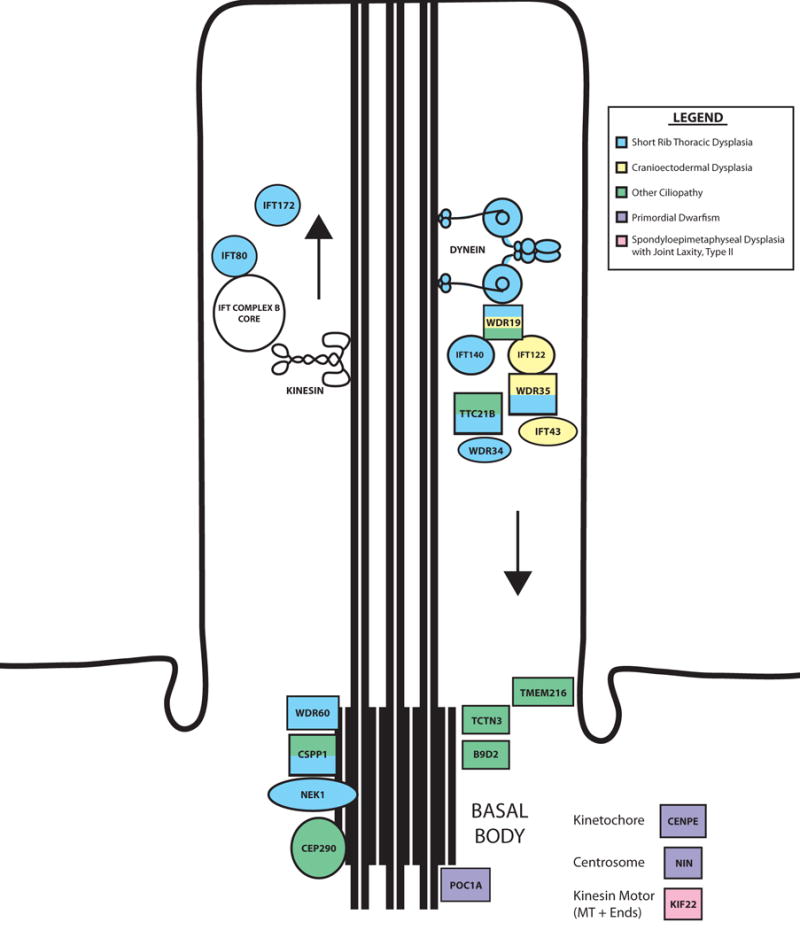
Components of the primary cilium are disrupted in many forms of skeletal dysplasia. These components include genes that encode parts of motor proteins (e.g., dynein) and parts of both the IFT-A and IFT-B complexes, which regulate retrograde and anterograde ciliary trafficking, respectively. The colors of the cilium components signify the types of disorders with which they are associated.
