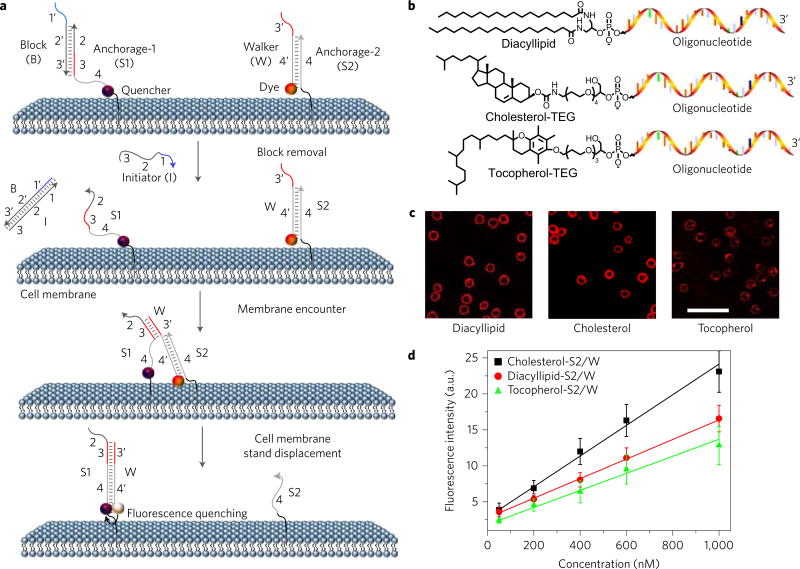
Figure 1. Anchoring and operation scheme of DNA probe on live cell membrane.
a, Schematic illustration of the operation of DNA probe on a live cell membrane. Here, the initiator (I) strand removes the block strand (B) by a strand displacement reaction. In this way, the translocation of the DNA probe (W) from one anchor site (S2) to another (S1) is triggered. b, Chemical structures of diacyllipid-, cholesterol- and tocopherol-conjugated oligonucleotides for membrane lipid domain studies. c, Confocal fluorescence microscopy images of carboxytetramethylrhodamine-labelled diacyllipid-, cholesterol- and tocopherol-conjugated S2/W conjugates (representative of six images). 500 nM of each conjugate was incubated with 5 × 105 Ramos cells at room temperature for 2 h, and unbound conjugates were removed. Scale bar, 50 µm. d, Flow cytometry evaluation of the anchoring efficiency of DNA probe on Ramos cell membranes. 0–1,000 nM initial concentrations of each conjugate were incubated with 5 × 105 Ramos cells at room temperature for 2 h, and unbound conjugates were removed. The error bars stand for the standard deviation from 5,000 cell events at each conjugate concentration.