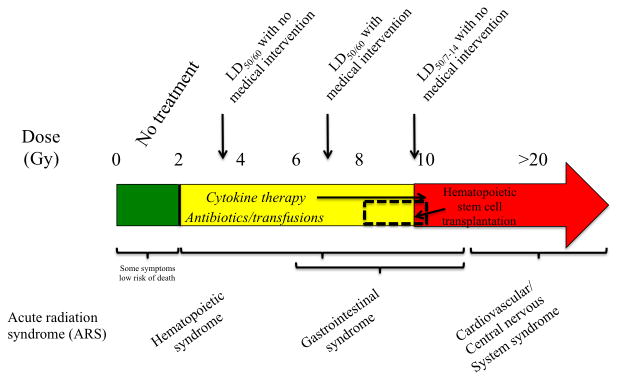
Figure 1.
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) in the human population is primarily divided in 4 different categories. Below 2 Gy, some individuals may experience some symptoms, such as emesis, however these individuals will not require immediate medical intervention for survival. Over doses of 2 Gy, individuals will experience and expire from myelosuppression (hematopoietic syndrome). The LD50/60 without medical intervention is ∼3.5 Gy, however with medical intervention it shifts upwards to ∼7 Gy. Only two medications have been FDA approved for the hematopoietic syndrome, Neupogen® and Neulasta®. Individuals exposed with a dose of 10 Gy and above will expire from gastrointestinal (GI) syndrome within 7-14 days post irradiation, although some individuals can have symptoms of GI syndrome with as low as 6 Gy. Individuals exposed to doses >20 Gy, although some can show symptoms as low as 10 Gy, will expire within days from cardiovascular and/or central nervous system syndromes. Since not all individuals can undergo an invasive procedure such as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, only a small percentage falling between a dose range that cannot adequately benefit from cytokine therapy and antibiotic treatments, will be candidates for such treatments. Sources for the information include (DiCarlo et al., 2011, Sullivan et al., 2013, CDC, 2015).