Figure 1. NRF2 promotes melanocyte viability.
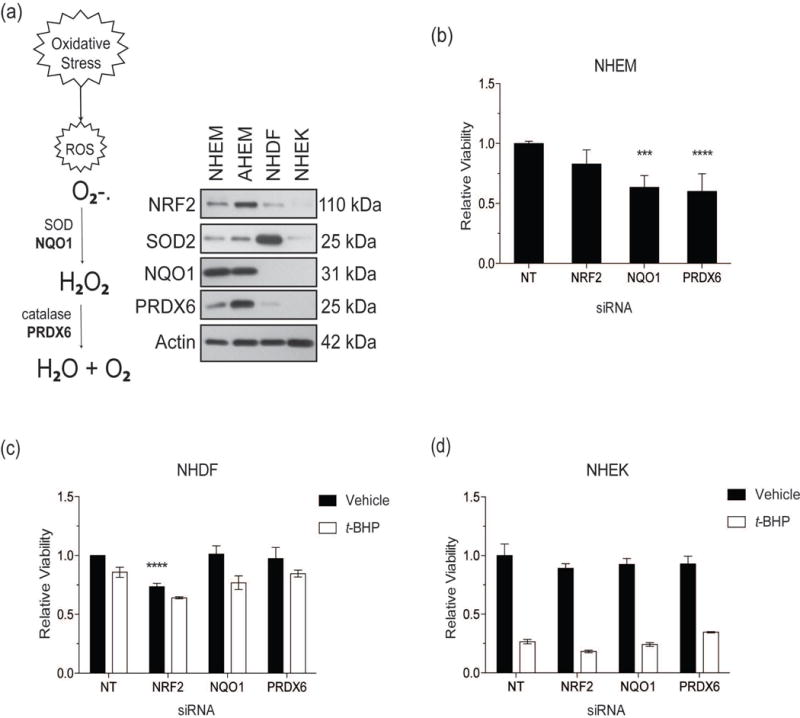
(a) The schema describes the process of ROS neutralization and highlights NRF2-targets, NQO1 and PRDX6 (in bold), that perform the same functions as generalized antioxidants. Total protein was extracted from four untreated cell lines derived from human skin. Cutaneous lines compared consisted of neonatal human epidermal melanocytes (NHEM), adult human epidermal melanocytes (AHEM), neonatal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) and neonatal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK). Protein levels of NRF2, SOD2, NQO1, PRDX6, and Actin (loading control) were measured by Western blot analysis. (b) NHEM were transfected with siRNAs against NRF2, NQO1, and PRDX6 and viability measured relative to non-target (NT) siRNA control. (c) NHDF and (d) NHEK were treated with siRNAs as in (b) in addition to t-BHP (250 μM) for 24 hours and viability measured relative to untreated NT siRNA control. Relative viability data are presented as mean ± SD, n=4 *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
