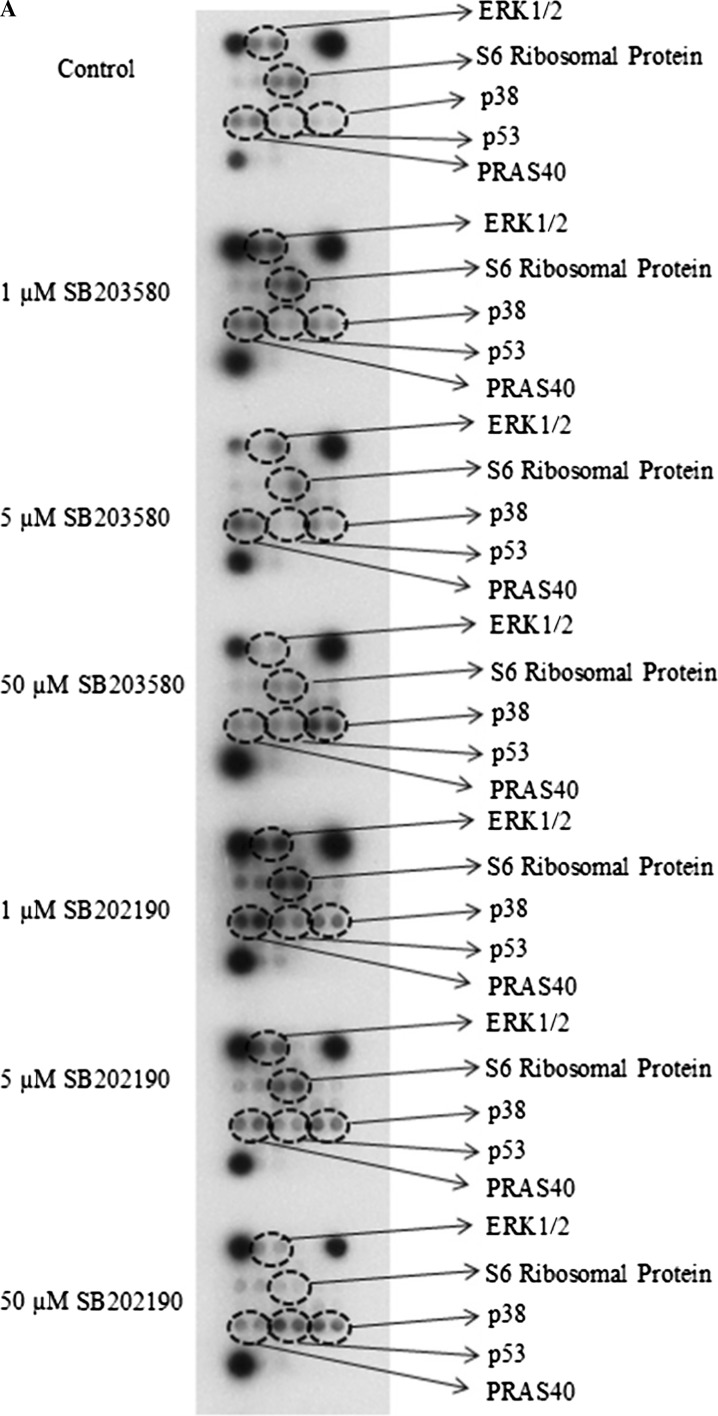
Fig. 5.

Effects of SB203580 and SB202190 inhibitors on intracellular signaling molecules. a MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells (200,000) were seeded in 60 × 15 mm sterile petri dishes. Cells were treated with 1 µM SB203580, 5 µM SB203580, 50 µM SB203580, 1 µM SB202190, 5 µM SB202190 or 50 µM SB202190 at the logarithmic phase of growth for 24 h. After inhibitor treatments, cells were lysed with ice-cold cell lysis buffer and then protein concentration was determined using the Bio-Rad dye-binding assay. The changes in the phosphorylation or cleavage of the indicated molecules were determined with the PathScan Intracellular Signaling Array Kit (Chemiluminescent Readout), according to the manufacturer’s procedure (Cell Signaling Technology), using 45 µg protein for each sample. Finally, the slide was incubated with Lumi-GLO/peroxide reagent for 2 min and exposed to Kodak BioMax X-ray films in dark room, b quantitation of mutant p53, ERK1/2, S6 Ribosomal Protein, PRAS40 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation. The quantitation was carried out by GelQuantNET program. The results are presented as fold changes/control. The experiment was performed twice with duplicate samples. The data are mean ± SEM (n = 4). Cntl, 0.5% DMSO-treated control group