Figure 2.
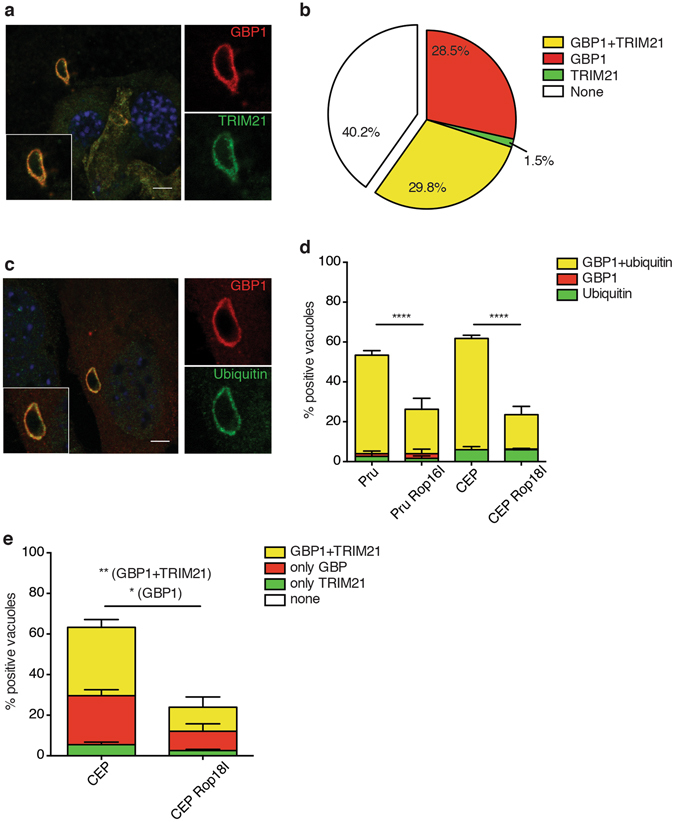
TRIM21 and ubiquitin are targeted to GBP1-positive type II Toxoplasma vacuoles in IFNγ-stimulated cells dependent on parasitic virulence factors. (a) Representative immunofluorescence confocal images of IFNγ-stimulated mouse embryonic fibroblasts infected 1 h with type II Toxoplasma and co-stained for GBP1 and TRIM21. Scale bar is 5 μm. (b) Quantification of GBP1 and TRIM21 co-recruitment to the parasite-containing vacuoles 1 h p.i. Data pooled from three independent experiments. (c) Representative immunofluorescence confocal images of IFNγ-stimulated mouse embryonic fibroblasts infected 1 h with type II Toxoplasma and co-stained for GBP1 and ubiquitin. Scale bar is 5 μm. (d) Quantification of ubiquitin- and/or GBP1-positive parasite-containing vacuoles in IFNγ-stimulated mouse embryonic fibroblasts infected 1 h with the canonical Toxoplasma type II (Pru) and type III (CEP) strains, as well as with Toxoplasma type II strain transgenic for the type I Rop16 (Pru Rop16I), and Toxoplasma type III strain transgenic for the type I version of Rop18 (CEP Rop18I). Data pooled from three independent experiments. Mean ± SEM, ****p < 0.0001, 2-way ANOVA. (e) Quantification of TRIM21- and/or GBP1-positive parasite-containing vacuoles in IFNγ-stimulated mouse embryonic fibroblasts infected 1 h with the canonical Toxoplasma type III (CEP) strain and Toxoplasma type III strain transgenic for the type I version of Rop18 (CEP Rop18I). Data pooled from three independent experiments. Mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, 2-way ANOVA.
