Figure 1.
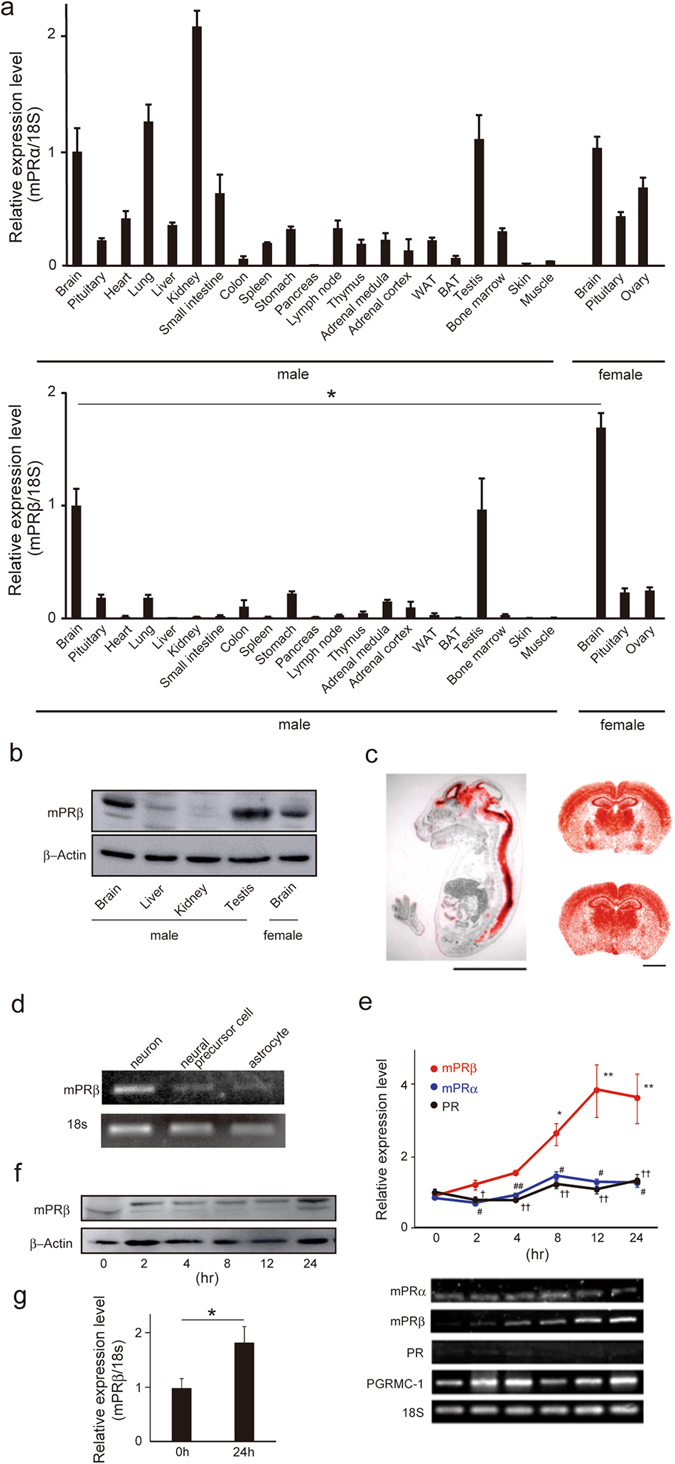
mPRβ is specifically expressed in the brain. (a) Expression of mPRα and mPRβ mRNA in mouse tissues (Post-natal day 49: P49) measured by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 3). WAT: White adipose tissue (epididymal adipose tissue), BAT: Brown adipose tissue. Control: 18S mRNA expression. Statistical analysis was performed by using Student’s t-test. (b) Expression of mPRβ protein in mouse tissues (Post-natal day 49: P49) measured by western blotting. β-actin protein expression was used as an internal control. (c) Localization of mPRβ mRNA in mouse embryos (E15.5, sagittal sections, Scale bar = 5 mm) and mouse brain (upper: male, lower: female, P49, coronal sections, Scale bar = 2 mm). They were examined by in situ hybridization with a 35S-labeled antisense mouse mPRβ RNA probe. Red grains superimposed on a hematoxylin-eosin stain indicate the localization of mPRβ mRNA. (d) mPRβ cDNA (about 600 base pairs) was detected in neurons, neural precursor cells, and astrocytes by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis followed by staining with ethidium bromide. 18S mRNA expression was used as an internal control. (e) The expression of the progesterone receptor was examined by quantitative RT-PCR in NGF-induced neuronal PC12 cells. (n = 3–6). *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01, compared with 0 h mPRβ; # p < 0.05, and ## p < 0.01, compared with mPRβ; † p < 0.05, and †† p < 0.01, compared with mPRβ (Tukey-Kramer). PR: Progesterone Receptor. (f) mPRb protein expression in NGF-induced neuronal PC12 cells. β-actin protein expression was used as an internal control. (g) Expression of mPRβ mRNA in NGF-induced neuronal SH-SY5Y cells. Statistical analysis was performed by using Student’s t-test. Results are presented as means ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05.
