Figure 5.
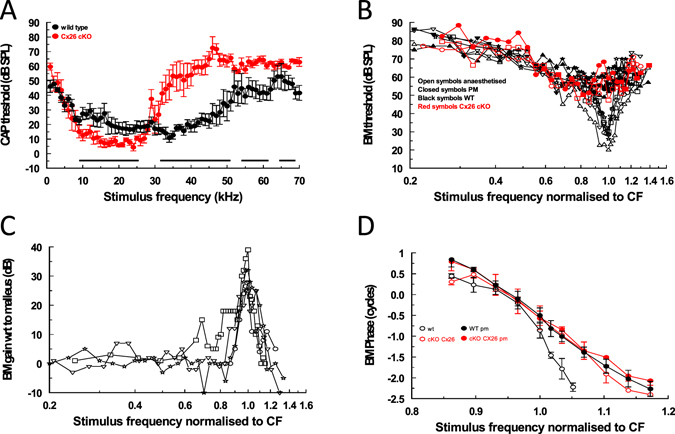
High-frequency hearing is desensitized and detuned and low-mid frequency hearing is sensitized in Cx26 cKO mice. (A) Compound action potential (CAP) audiogram (mean ± SD of CAP detection threshold as a function of stimulus frequency) from 5 WT (black symbols) and 5 Cx26 cKO (red symbols) mice. Solid horizontal lines indicate regions where CAP thresholds of WT and Cx26 cKO mice are significantly different (unpaired t-test, 0.05 two-tailed p value). (B) Threshold (0.2 nm) frequency tuning curves measured from the 54 kHz–59 kHz frequency region of the basal turn BM from 5WT, and 2 Cx26 cKO mice, anaesthetized and post-mortem. The frequency axes represent the stimulus frequency normalised to the characteristic frequency (CF) of the measurement location. Different symbols indicate different preparations. (C) Gain of BM displacement as a function of stimulus frequency (normalised to the CF of the measurement location) relative to malleus displacement for 4 WT mice. (D) BM phase as a function of stimulus frequency (normalised to the CF of the measurement location) measured from the 54 kHz–59 kHz frequency region of the basal turn BM from 5WT, and 5 Cx26 cKO mice, anaesthetized and post-mortem. All mice used in the study were 21–26 day post-partum.
