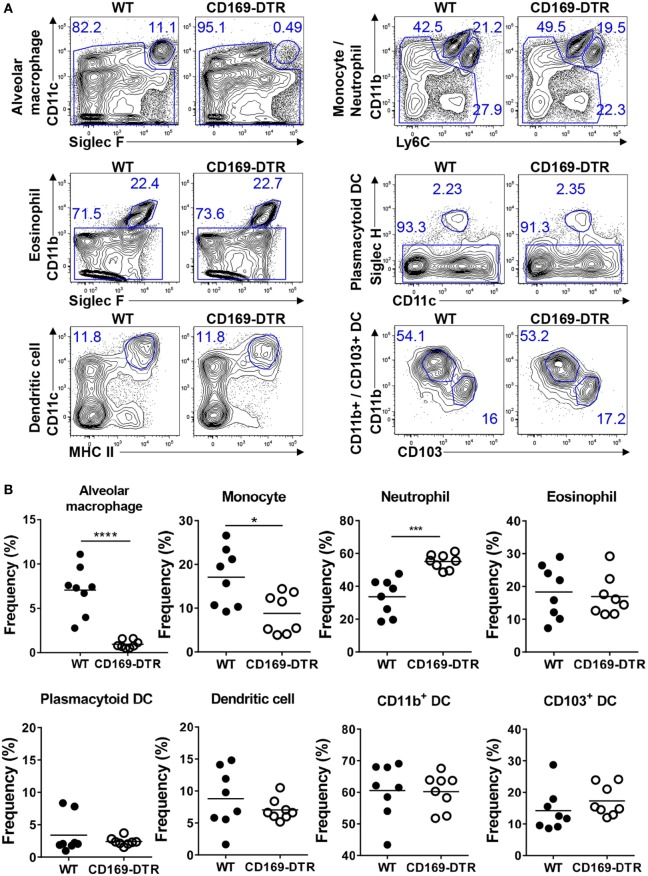
Figure 1.
Diphtheria toxin (DT) administration to CD169-diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) mice induces alveolar macrophage (AM) depletion and reduces monocyte recruitment. (A) Lung cells isolated from wild-type (WT) and CD169-DTR mice 1 day after DT treatment were stained with the indicated antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. AMs, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, dendritic cells (DCs), CD11b+ DCs, and CD103+ DCs were defined by their surface marker expression. The gating strategy is described in Figure S1 in Supplementary Material. (B) Results are shown as dot graphs. Each dot represents an individual mouse (n = 8 in each group). Statistically significant differences are indicated: *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Data are representative of three independent experiments.