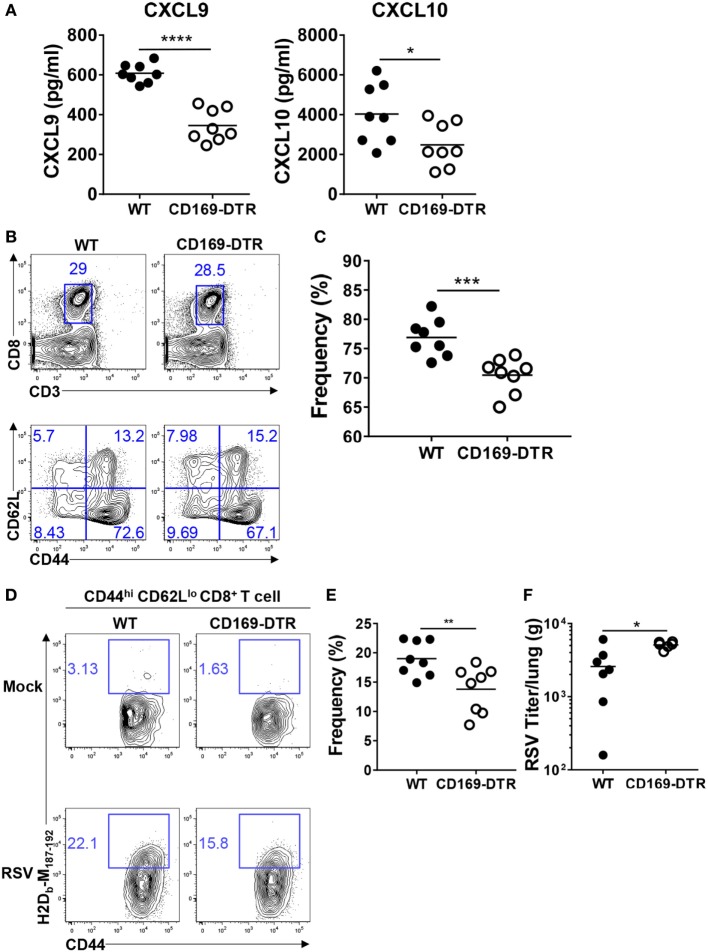
Figure 6.
CD169+ cell depletion reduces the recruitment of effector CD8+ T cells in lungs after respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. At the indicated time points after RSV infection, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was collected from diphtheria toxin-treated wild-type (WT) and CD169-diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) mice. The levels of CXCL9 and CXCL10 in the lavage fluids were measured by ELISA (A). Seven days after RSV infection, the frequencies of CD8+ T cells (B) and CD44hi CD62Llo CD8+ T cells (C) were assessed by flow cytometry. (D) RSV M peptide-specific CD44hi CD62Llo CD8+ T cells were detected by flow cytometry. (E) Frequencies of CD44hi CD62Llo tetramer+ CD8+ T cells were quantified from flow cytometry data of RSV-infected mice. (F) Five days after infection, RSV viral titers from lung homogenates were measured on HEp-2 cells. Each dot represents an individual mouse (n = 8 in each group). Statistically significant differences between groups are indicated: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. Data are representative of two independent experiments.