Figure 1.
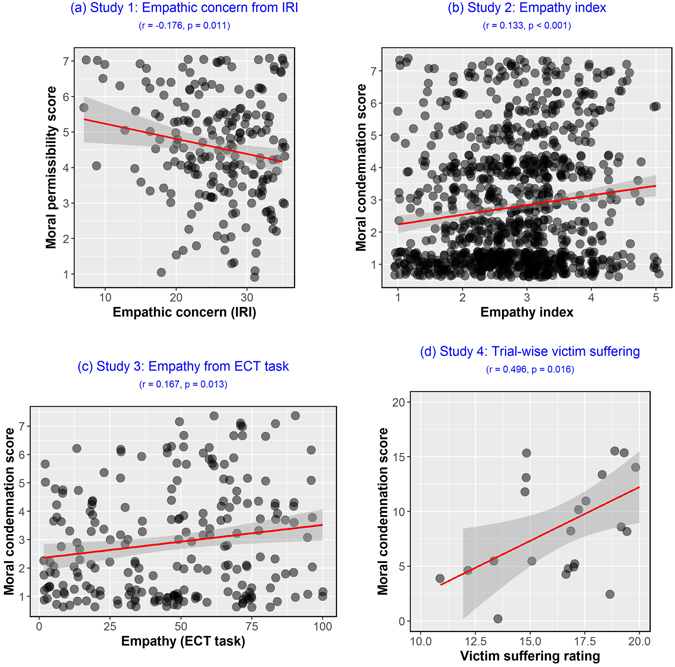
Positive relationship between empathy and condemnation of accidents. Behavioral studies 1–4 revealed that individuals who scored high on empathy, as assessed using (a) empathic concern (EC) subscale of Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI), (b) Empathy index measure, (c) empathy scores from the Empathy-Compassion Task (ECT), and (d) trial-by-trial victim suffering ratings, condemned accidental harm-doers more severely. Different questions were asked across studies 1–4: (a) moral permissibility, (b,c) wrongness and punishment, and (d) acceptability and blame.
