Figure 2.
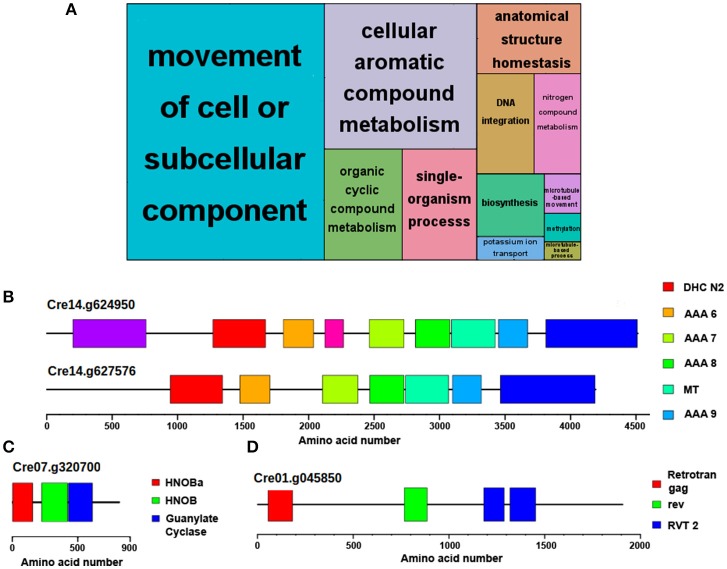
Functional annotation of genes exclusively identified in Chlamydomonas. No potential Ostreococcus or Arabidopsis orthologues were identified for 15% of Chlamydomonas proteins. (A) Non-redundant GO term enrichment analysis over the set of Chlamydomonas genes with no potential orthologue in the other species, suggesting that they are mainly involved in “movement of cell or subcellular component,” “organic cyclic compound metabolism,” and “DNA integration”. Each rectangle area in the treemap represents the −log10 (p-value) for the corresponding GO-term. (B) Domain structure of the proteins encoded by Flagellar inner arm dynein 1 (Cre14.g624950) and axonemal dynein heavy chain 6 (Cre14.g627576), two Chlamydomonas-specific flagellar proteins absent in Ostreococcus and Arabidopsis involved in “movement of cell” or “subcellular component.” (C) Domain structure of class III guanylyl and adenylyl cyclase encoded by CYG11 (Cre07.g320700), a Chlamydomonas-specific protein involved in “organic cyclic compound metabolism.” This protein shows a higher homology to animal cyclases than to plant ones. (D) Domain structure of the protein encoded by gag-pol-related retrotransposon (Cre01.g045850), an example of Chlamydomonas specific proteins associated to the “DNA integration” GO term. Color boxes represent domains identified in pfam database including their identification codes.