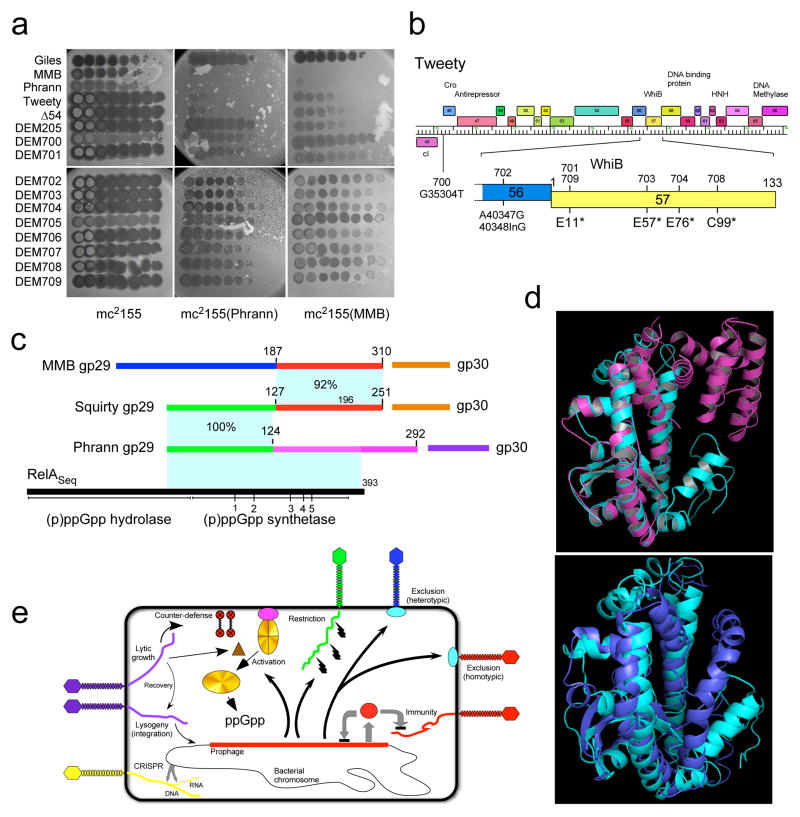
Figure 6. Mechanisms of prophage-mediated defense against viral attack.
(a) Ten-fold serial dilutions of Defense Escape Mutant (DEM700-DEM709) derivatives of a TweetyΔ54 parent that overcome Phrann defense were spotted on wild type M. smegmatis (mc2155) or Phrann and MMB lysogens. All platings were performed in at least two separate experiments. (b) Tweety Δ54 DEM mutants map in early lytic genes. Genome sequencing shows DEM 700-series mutants map in Tweety early lytic genes. DEM706 and DEM707 are siblings of DEM701 and DEM702, respectively (see text and Supplementary Information for details; Supplementary Figure 22). (c–e) Relationships among phage-encoded (p)ppGpp synthetase-like proteins. (c) Phrann gp29 is a homologue of RelA/SpoT proteins with similarity to the (p)ppGpp synthetase domain of Streptococcus equimilis RelA including 5 conserved motifs (1–5)37. The Cluster F phage Squirty encodes a related protein (gp29) sharing the N-terminal 124 residues with Phrann gp29, but with divergent C-termini. MMB gp29 is not predicted by HHpred to be related to RelSeq, but shares its C-terminus with Squirty gp29. MMB gp30 and Squirty gp30 are closely related and are both predicted to be membrane localized. (d) I-TASSER38 alignment of Phrann gp29 (top, cyan) to Streptococcus equimilis RelA (PDB: 1vj7A, magenta; TM-score 0.539) and to a PHYRE239 structural prediction of Phrann gp29 (bottom, cyan). (e) Models for prophage-mediated viral defense. An integrated prophage (red line) confers defense against viral attack through numerous mechanisms, either homotypically (i.e. against the same or closely viruses) or heterotypically (against unrelated phages). Homotypic defense includes repressor-mediated immunity (repressor, red circle) and superinfection exclusion (blue circle) against itself (red phage). Heterotypic defense includes an exclusion-like system illustrated by Charlie gp32 defense against Che9c (blue phage), and restriction against many viruses (illustrated by the green phage) by Panchino gp28. Defense is also mediated by a predicted (p)ppGpp synthetase (e.g. Phrann gp29; gold circle), which we propose is kept in an inactive form (gold circle with crossed lines) by an inhibitor (purple circle), which for Squirty gp30 is membrane located. Lytic growth by specific phages activates the defense through early lytic protein, which is proposed to dissociate the (p)ppGpp synthetase from its inhibitor, enabling rapid accumulation of (p)ppGpp and growth arrest. Tweety encodes a counter-defense system (gp54) that may prevent activation of (p)ppGpp synthesis.