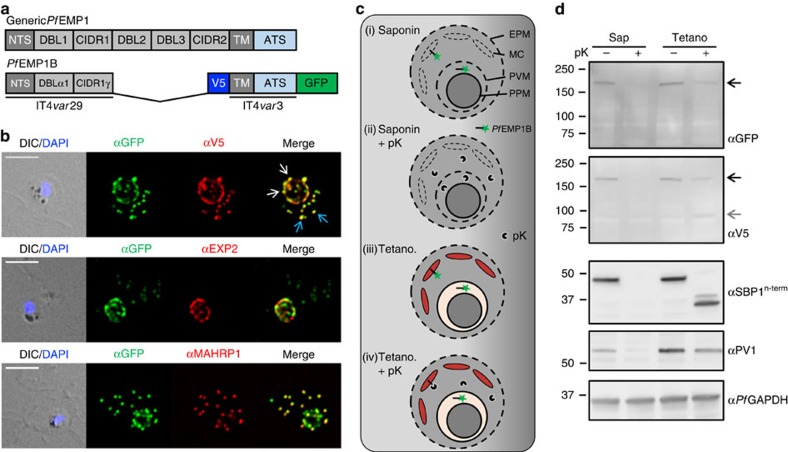
Figure 1. Location and protease accessibility of PfEMP1B during export.
(a) Schematic of the minimal PfEMP1 construct, PfEMP1B, used in this study. PfEMP1B contains the semiconserved head structure from IT4var29, an internal V5 epitope tag, a transmembrane (TM) domain and acidic terminal segment (ATS) from IT4var3 followed by GFP. Structure of a generic PfEMP1 molecule is shown above. (b) Immunofluorescence analysis of PfEMP1B-infected RBCs labelled with antisera recognizing GFP (green) and V5 or EXP2 or MAHRP1 (red). Differential interference contrast (DIC) image and parasite nuclei (stained with DAPI; blue) are shown on the left. White arrows indicate PV-localized PfEMP1B while blue arrows indicate PfEMP1B located at the Maurer’s clefts. Scale bars, 5 μm. (c) Schematic of the protease protection assay performed on PfEMP1B-infected RBCs. Cells were first treated with either saponin, to permeabilize the RBC membrane, the Maurer’s clefts and PVM or with Tetanolysin (Tetano) to permeabilize only the RBC membrane, and then incubated in the presence or absence of proteinase K (pK). (d) Western blots of the protease-treated infected RBCs were probed with anti-GFP and anti-V5 antisera. SBP1, PV1 and PfGAPDH western blots are shown as controls. Full-length PfEMP1B is indicated with a black arrow and the truncated product with a grey arrow. Molecular masses are shown in kDa. Uncropped western blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12.