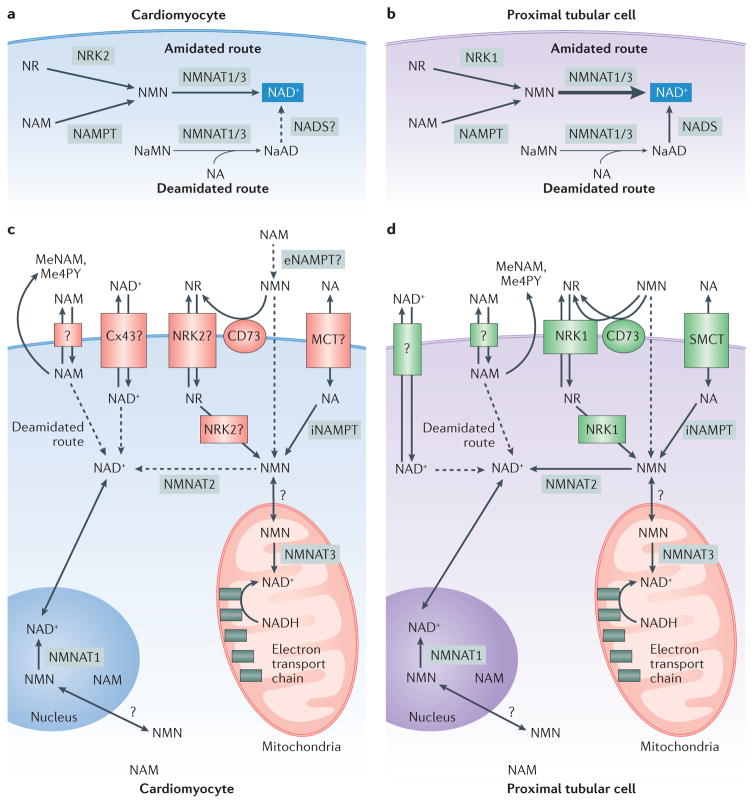
Figure 1. Cardiac and renal biosynthesis and the metabolome of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
Two routes of NAD+ synthesis — deamidated (de novo synthesis) and amidated (precursor salvage) — occur in the heart (parts a,c) and the kidney (parts b,d) (REF. 8). In the amidated route, which dominates in both tissues, the activities of nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK) isoforms (NRK2 in the heart and NRK1 in the kidney) enable generation of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) from the salvage of nicotinamide riboside (NR), whereas nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) activity converts salvaged nicotinamide (NAM) to NMN. Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenyltransferase (NMNAT) isoforms 1 (nuclear) and 3 (mitochondrial) convert NMN to NAD+ in the amidated route and nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) to nicotinic acid dinucleotide (NaAD) in the deamidated route. The activities of NMNAT1/3 in the amidated route are much greater in the kidney (part b) than in the heart (part a), as indicated by the arrow thicknesses. Nicotinic acid (NA) can also be converted to an intermediate in the deamidated route, and the activity of NAD synthase (NADS) enables conversion of NaAD to NAD+, although the role of NADS in the heart is speculative. Uptake of NAD+ and its precursors occurs through many means in the heart (part c) and kidney (part d). NAD+ can be directly transported into the heart by the connexion 43 hemichannel (Cx43). Renal uptake of NA occurs through the sodium monocarboxylate transporter (SMCT) (REF. 14). NR and NMN require NRK1 for optimal uptake and conversion to NAD+ in the kidney20. NRK2 might serve this role for these NAD+ precursors in the heart. Additionally, extracellular NMN might be converted into NR by membrane bound cluster of differentiation 73 (CD73) (REF. 19) and subsequently taken up by renal NRK1 or cardiac NRK2. Renal NAM uptake is thought to occur through an unidentified transporter14. NAM — generated from exogenous sources or other NAD+ precursors such as NA — is maintained at low levels in the heart and kidney9 through its conversion into the byproducts 1-methylnicotinamide (MeNAM) and N-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide (Me4PY), which are excreted by the cell. 5′-ectonucleotidase; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; NADH, reduced NAD.