Fig. 6. SYNCRIP’s post-transcriptionally controls HOXA9 protein expression.
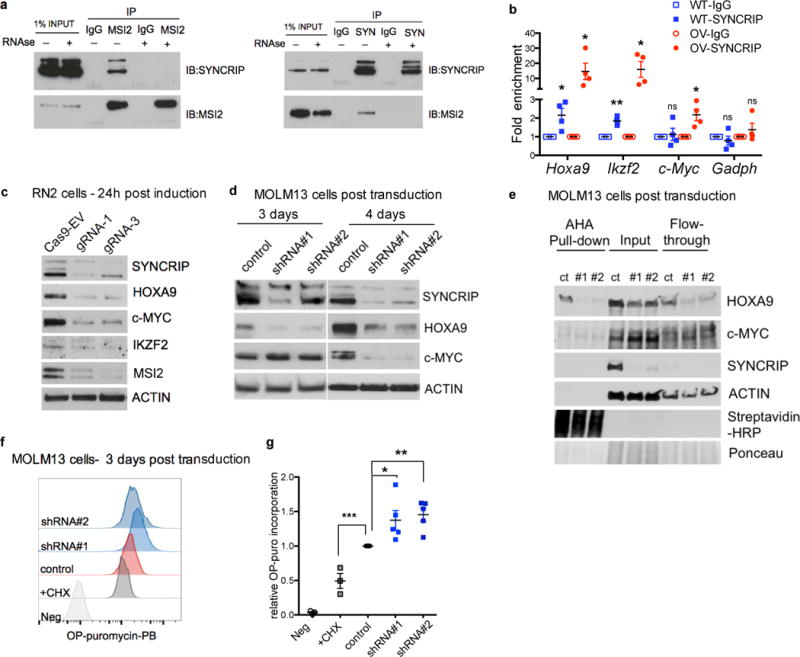
(a) Human myeloid leukemia K562 cells overexpressing MSI2 were immunoprecipated with endogenous MSI2 and SYNCRIP. Lysates incubated with RNase were then immunoprecipated indicating SYNCRIP-MSI2 interaction is RNA mediated. (b) SYNCRIP was immunoprecipiated with IgG or SYNCRIP antibody in either endogenous (WT) or human SYNCRIP overexpressing (OV) mouse RN2 MLL-AF9 leukemia cells. n=4 independent experiments; error bars, s.e.m. * p<0.05, **p<0.001 two tailed t test. (c) Immunoblots showing downregulation of HOXA9, c-MYC and IKZF2 proteins upon SYNCRIP knocked down in RN2 cells. (d) Immunoblots showing expression level of HOXA9 and c-MYC upon SYNCRIP-KD in human MOLM13 leukemia cells 3 and 4 days post transduction with viruses expressing control shRNA and SYNCRIP-shRNAs together with GFP. (e) Immunoblots showing protein level of SYNCRIP, HOXA9 and c-MYC in AHA-pull down fraction, input and flow through fraction. AHA incorporation into newly synthesized HOXA9 (but not c-MYC) proteins was reduced in SYNCRIP-KD cells. Streptavidin-HRP, Ponceau staining and ACTIN serve as control for total protein input and loading control. (f) Representative histograms analysis of OP-Puro incorporation in control and SYNCRIP-KD MOLM13 cells (shRNA#1 and shRNA#2). (g) Quantitative summary of relative OP-Puro incorporation in cells in (f). CHX-treated cells were used as negative control (n=3). Cells without OP-Puro incorporation served as staining control. n=4 independent experiments; error bars, s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0001 two tailed t test.
