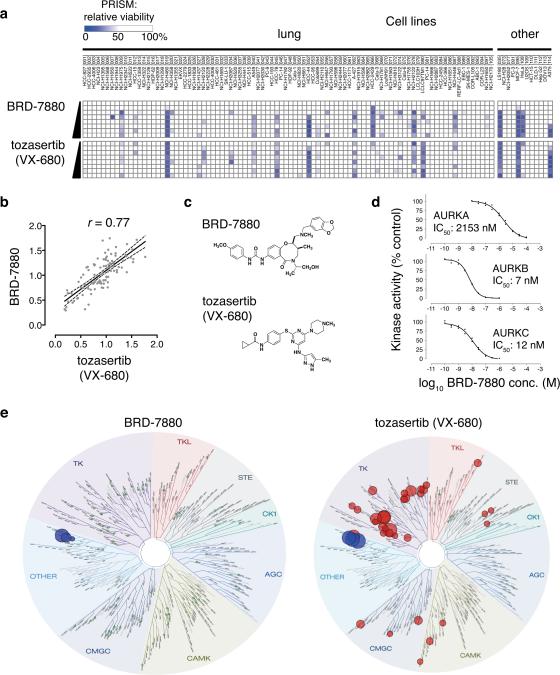
Figure 3. BRD-7880 inhibits aurora kinase B.
a. Comparison of PRISM profiles across 102 cell lines for BRD-7880 (0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 μM) or tozasertib (0.07, 0.13, 0.26, 0.52, 1, 2, 4, 8 μM).
b. Correlation of PRISM AUC between BRD-7880 (a.k.a. BRD-K01737880) and tozasertib. Area under the curve (AUC) of viability vs. concentration curve was calculated for each cell line across 8 doses of compound. Least-squares (ordinary fit) regression line is shown with 95% confidence bands. Spearman r = 0.77.
c. Structures of BRD-7880 and tozasertib.
d. In vitro aurora kinase assays. Incorporation of radioactivity from 10 μM γ-33P-ATP was measured in in vitro kinase assays across 8 doses in duplicate by the EMD Millipore KinaseProfiler service under published standard conditions with 10 mM ATP. Full-length human AURKA was assayed with 200 μM LRRASLG (Kemptide); full-length human AURKB with 30 μM AKRRRLSSLRA (ribosomal protein S6 peptide); and full-length human AURKC with 30 μM AKRRRLSSLRA. IC50 values were modeled using least-squares and variable slope with GraphPad Prism 6.0 software.
e. KinomeScan profile for BRD-7880 across 98 kinases. Left, schematic representation of relative affinity of BRD-7880 for specific kinases in the KinomeScan assay (data available in Supplementary Table 9). Green circles represent tested kinases for which BRD-7880 decreases binding < 75% control. Right, published relative affinities of tozasertib (VX-680) for same 98 kinases (where available 26, 27).