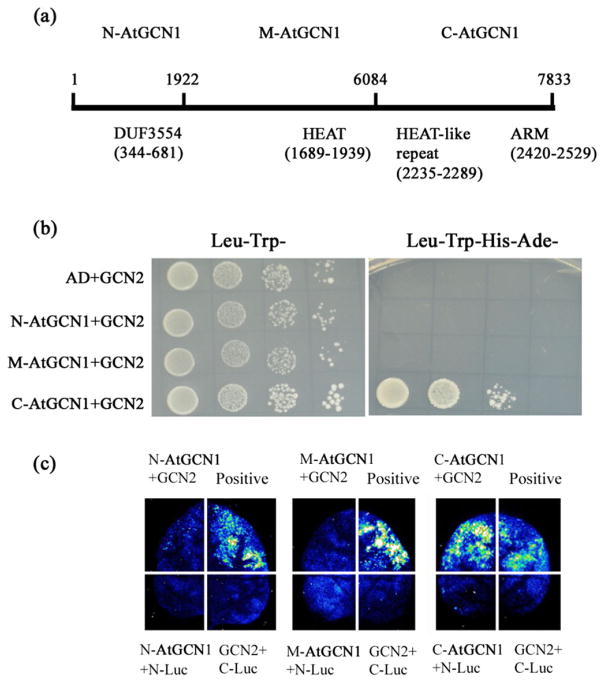
Figure 2.
Interaction between AtGCN1 and GCN2. (a) The AtGCN1 CDS sequence was divided into three fragments: N-AtGCN1 (1–1922 nt), M-AtGCN1 (1923–6084 nt) and C-AtGCN1 (6085–7833 nt). The motifs identified in AtGCN1 are described below the black line. (b) The C-terminal of AtGCN1 interacts with GCN2 in yeast. AD, the empty pGADT7 vector; N-AtGCN1, the N-terminal region of AtGCN1 fused with AD; M-AtGCN1, the middle part of AtGCN1 fused with AD; C-AtGCN1, the C-terminal region of AtGCN1 fused with AD. GCN2 was fused with pGBDT7. Leu− Trp− represents SD medium without Leu and Trp, and Leu−Trp− His−Ade− represents SD medium without Leu, Trp, His and Ade. (c) The firefly luciferase (LUC) images of N. benthamiana leaves expressing the fusion genes. N-Luc, N-terminal fragment of Luc; C-Luc, C-terminal fragment of Luc; N-AtGCN1, N-terminal region of AtGCN1 fused with C-Luc; M-AtGCN1, the middle region of AtGCN1 fused with C-Luc; C-AtGCN1, C-terminal region of AtGCN1 fused with C-Luc. GCN2 was fused with N-Luc. The positive interaction between OST1-C-Luc and ABI1-N-Luc was used as a control.