FIGURE 7.
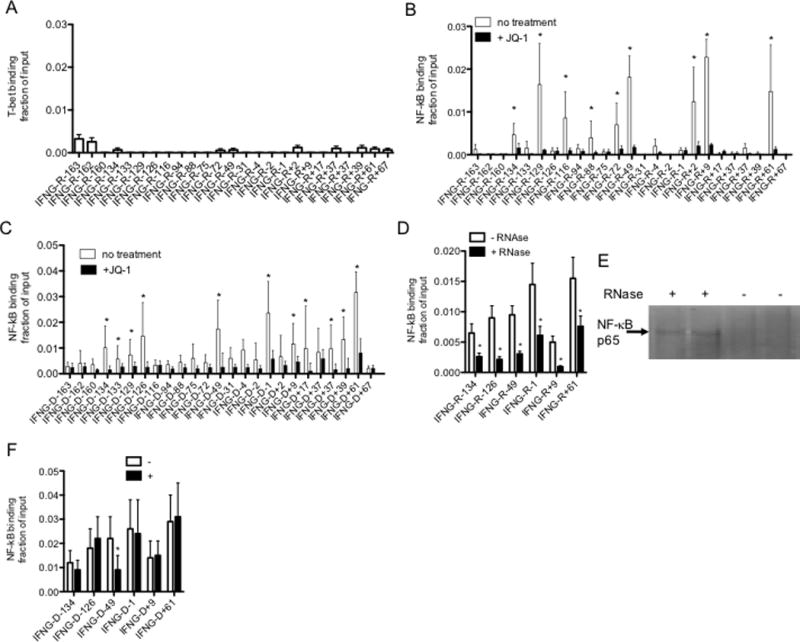
IFNG-associated lncRNAs bind NF-κB. (A&B) Cells were cultured with or without JQ1 (150 nM, 4 hr) and lysed. After lysis, (A) anti-T-bet and (B) anti-NF-κB, p65 subunit, immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed. Levels of each IFNG-R-lncRNA in the anti-T-bet, anti-NF-κB, p65 subunit, and isotype control immunoprecipitates were determined by PCR. Results are expressed as fraction of input of the indicated IFNG-associated novel lncRNAs relative to totals of each IFNG-R-lncRNA. Levels of IFNG-R-associated lncRNAs in the isotype control immunoprecipitates were negligible and therefore not included in the calculations. Error bars are S.D of 8 independent experiments, *=P < 0.05. (C) As in (B) except ChIP assays were performed to measure NF-κB, p65, binding to IFNG genomic locus sites. Results are expressed as fraction of input relative to an isotype control. Error bars are S.D of 5 independent experiments, *=P < 0.05. (D) Chromatin was isolated from TM cells by lysis in non-ionic detergents and treated with RNase, 10 min, RT. Chromatin was cross linked with formaldehyde and processed for ChIP assays. NF-κB, p65 binding is expressed as fraction of input, N=3, *=P < 0.05 comparing treated and untreated samples. (E) After RNAse treatment, chromatin was pelleted by centrifugation and supernatant fluids harvested and analyzed for NF-κB protein by western blotting. The arrow indicates the p65 subunit of NF-κB. (F) Cells were transfected with the siRNA targeting IFNG-R-49 (+) or a scrambled control siRNA (−) and cultured for 24 hr. Cultures were fixed with paraformaldehyde, harvested and processed for ChIP assays using an NF-κB, p65 subunit, antibody. The Y-axis shows NF-κB, p65 subunit, binding as fraction of input at the indicated IFNG genomic loci, X-axis.
