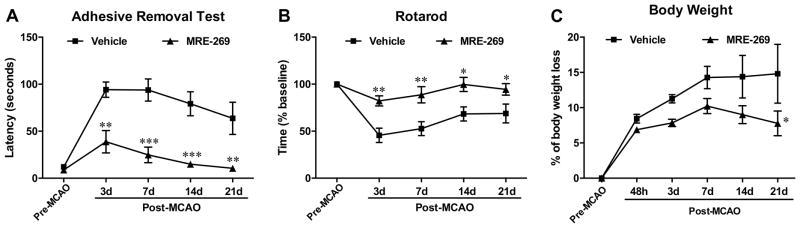
Figure 2. Effect of MRE-269 on neurological function and body weight loss in aged rats subjected to transient MCAO.
The drug was given as detailed in the legend of Fig. 1, and neurobehavioral analyses and body weight measurement were performed at pre- and post-MCAO. The same animals were MRI-scanned at 48 h and at 21 days (data presented in Fig. 1). Delayed MRE-269 treatment significantly improved long-term neurological outcomes assessed by adhesive removal test (A) and rotarod (B) compared to the vehicle group from day 3 to day 21 after MCAO. C) Bar graphs showing body weight loss was continuously increased from 48 h to day 21 after MCAO in the vehicle group, but MRE-269 treatment significantly attenuated body weight loss after one week following MCAO. Data in panels A to C were expressed as mean ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 versus vehicle. Vehicle, n=8; MRE-269, n=9.